How to Sit With SI Joint Pain? Best Ways
Medically reviewed by our experts


You are probably uncomfortable and wondering how to sit with SI joint pain. SI joint discomfort can be a distressing illness that interferes with everyday activities such as sitting. Inflammation or dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint can cause pain in the lower back, hips, and buttocks. Sitting for extensive amounts of time might aggravate the discomfort and make achieving an appropriate sitting position difficult.
Addressing SI joint discomfort when sitting necessitates a combination of measures for reducing joint tension and promoting correct positioning and posture. Maintaining appropriate posture is one of the first steps to alleviating SI joint pain. Sit on the chair with your back straight, shoulders at ease, and buttocks properly distributed. Avoid hunching over or slumping to one side, as this might put a strain on the SI joint.
In some circumstances, placing pillows or cushions beneath the buttocks or between the knees might assist in reducing strain on the SI joint as well as offer additional support. Test with various positions and supports to see what works best for your particular pain.
Sitting with SI joint pain requires careful posture, regular pauses, and extra support. Nevertheless, it is critical to seek the advice of a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment of your specific illness. They can suggest specific exercises, therapies, or additional treatments to reduce pain and enhance healing.
While focusing on the SI joint, it’s also helpful to recognize the importance of overall joint health, including understanding what bones make up the knee joint—the femur, tibia, and patella. This knowledge can aid in comprehending how interconnected our musculoskeletal system is and the importance of holistic joint care.
What Is the Sacroiliac?
The sacroiliac (SI) joint joins the sacrum and the ilium and is vital in human anatomy. The sacrum is a triangular-shaped bone near the base of the spine made up of five connected vertebrae. The ilium is the top region of the pelvis, where the wings on each side develop. The location of the SI joint lies on both sides of the lower back, where the sacrum and the ilium meet.
The SI joint’s primary purpose is to pass on forces between the upper body and the legs. It offers stability and support, particularly during weight-bearing activities like walking, jogging, and standing. The SI joint transfers forces generated by the upper body to the lower parts of the body.
Although the SI joint is relatively inert compared to other joints in the body, it allows some movement. This movement is critical for adapting the body’s natural biomechanics and absorbing trauma. The joints have cartilage coverings on their surfaces, enabling smooth movement and reducing friction between bones.
Consider using an ergonomic chair or adjustable seat that allows you to alter the position and support when sitting for long periods of time. Adjust the chair’s height and tilt to preserve a balanced spine posture and reduce pressure on the sacrum sitting.
Pain and discomfort can result from SI joint dysfunction or inflammation. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction, often known as SI joint discomfort, can cause pain in the lower back, hip, and buttock areas. It can also cause discomfort extending down the legs. Trauma or injury, pregnancy-related hormone changes, arthritis, muscle imbalances, or repetitive stress can all lead to SI joint dysfunction.
It is critical to correctly diagnose SI joint discomfort in order to discover its root cause and develop a suitable treatment approach. Physical therapy, chiropractic care, pain management strategies, activities to strengthen the surrounding muscles, and, in certain situations, surgery, are all suitable treatment alternatives.
What Causes Sacroiliac (SI) Joint?
A variety of factors might lead to the occurrence of SI joint dysfunction or discomfort. While determining the precise root cause of SI of this condition might be challenging, it frequently stems from a combination of factors. Here are a few examples of common causes:
- Trauma: Any damage or trauma to the SI joint, for instance, a fall, automobile accident, or sports injury, may interfere with the joint’s normal functioning. Traumatic occurrences can result in ligament sprains, fractures, or dislocations, resulting in SI joint dysfunction.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes prompt the ligaments surrounding the SI joint to relax in preparation for childbirth. This greater movement might cause pain or instability in the SI joint. Furthermore, the extra weight and changing pregnancy posture might strain this body part even more.
- Degenerative Alterations: As with other joints, wear and tear on the SI joint can contribute to degenerative changes over time. These changes could result in cartilage loss, the production of bone spurs, or the emergence of joint dysfunction.
- Arthritis: Arthritis is a disorder characterized by joint inflammation and deterioration. Arthritis of the SI joint can cause discomfort, stiffness, and reduced versatility in motion. Some of the rheumatic arthritis that can affect the SI joint are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
- Muscle Imbalances or Weakness: Muscular abnormalities in the hips, pelvis, or spine can impair the SI joint’s stability and alignment. Weakness or tightness in specific muscle groups might result in an unequal distribution of forces, which can cause SI joint pain.
- Repetitive Pressure or Overuse: Activities such as extended standing, walking, or running that entail repetitive movements or excessive tension on the SI joint can strain it and cause discomfort and dysfunction.
Various factors, ranging from traumas and medical problems to lifestyle and postural concerns, can cause sacroiliac joint dysfunction and pain. Proper diagnosis and care, which may involve physical therapy, pain medication, or surgical intervention in extreme cases, can help reduce symptoms and enhance SI joint function.
Understanding how to improve joint health is vital for managing SI joint pain effectively. Incorporating a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hydration into your lifestyle can enhance your overall joint function and resilience, providing a solid foundation for reducing SI joint discomfort
How to Sit With SI Joint Pain?
Proper posture is critical to maintaining a healthy musculoskeletal structure and is especially vital while coping with SI joint pain. The SI joint links the sacrum to the pelvis at the base of the spine, providing stability and transmitting forces between the upper and lower limbs. Incorrectly sitting can aggravate the pain and anguish when the SI joint is inflamed or injured.
Slouching or sitting with a rounded back for extended periods of time can put more pressure on the SI joint, causing further irritation. Therefore, understanding how to sit with SI joint pain can help decrease symptoms and promote recovery. Below are some of the ways you can avoid sacrum pain sitting.
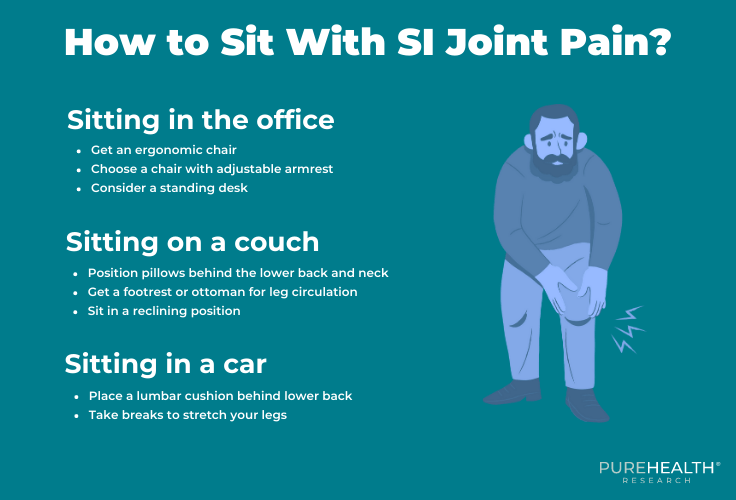
Sitting on an Office Chair & Conference Room Chairs
You can use numerous approaches to deal with SI joint pain while sitting in office chairs or conference room seats. For starters, consider utilizing an ergonomic chair with sufficient lumbar support. Adjust the chair’s height and tilt to find a comfortable posture that balances your spine and pelvis.
To support your arms and shoulders, choose a chair with adjustable armrests. Adjustable seats are prevalent in businesses, so take advantage of them to avoid putting strain on your back.
Alternatives to standard office chairs, such as standing desks or kneeling chairs, can also ease the strain on the SI joint. Also, make sure the desk is at elbow length. Standing up and moving about throughout the day can also help ease discomfort and maintain joint mobility. Carrying out these activities is paramount to maintaining balance and ensuring one does not strain their back.
In addition to ergonomic adjustments, integrating vitamins for cracking knees into your daily regimen can further support joint health. Essential nutrients like Vitamin D and Vitamin E are crucial for maintaining healthy bones and reducing inflammation, potentially alleviating some discomfort associated with SI joint pain.
Sitting on a Couch
Sitting on a couch for long periods can lead to bad posture and discomfort. Therefore, supporting yourself using pillows positioned adequately behind the lower back and neck is critical to ease sacrum pain from sitting. Doing this helps to keep the spine’s natural curve and relieves strain on the back muscles. In addition, you can elevate and support your legs or feet with pillows, enabling greater blood circulation and alleviating pressure.
A footrest or ottoman is another way to enhance leg circulation and minimize strain. They usually ensure one can switch from one posture to another while sitting. In addition, taking breaks to stand up, stretch, and walk around can improve general well-being. Consider sitting in a reclining position on the couch to relieve strain on the SI joint. However, keep excellent posture in mind so as to prevent slouching or sinking excessively into the cushions.
Sitting in a Car
If you suffer from SI joint pain sitting while driving, it is critical to prioritize comfort and support. Long drives can be stressful on the body, but there are ways to make them more comfortable. Check that the car seat has enough lumbar support. Place a lumbar cushion or rolled-up towel behind your lower back to retain the spine’s natural curve and prevent stress on the SI joint.
During long journeys, take frequent pauses to stretch your legs, walk about, and relieve pressure on the SI joint to improve blood circulation. Adjust the seat position to support your back and knees slightly higher than your hips. Adjust the seat, steering wheel, and mirrors as necessary to achieve a comfortable driving posture and reduce the chance of discomfort or weariness. Use your car’s lumbar support and seat adjustments to find a sitting position that reduces SI joint discomfort.
Sitting at a Dining Table
Pay attention to the chair height when sitting at a dining table if you suffer from SI joint pain. Having adjustable seats is a plus since it helps you change positions every now and then or once you feel a strain on your lower back. Consider a chair that enables you to sit with your feet flat on the ground and your knees at a 90-degree angle. This posture aids in the maintenance of appropriate alignment and decreases strain on the SI joint.
Avoid sitting in one posture for long periods of time. Occasionally shift your weight, modify your posture, and take small breaks to walk, stand up, and stretch, especially during long eating periods. Supportive seat cushions can also enhance comfort and relieve pressure on the SI joint. While dining, keep an upright posture and avoid drooping or leaning forward, as this can increase SI joint pain.
How to Stand With SI Joint Pain
Maintaining a proper standing posture is critical to decreasing discomfort and promoting healing when dealing with SI joint pain. Here are some pointers to assist you when standing:
- Align Your Body: Stand straight with your head, shoulders, and hips in an upright position. Avoid bending over or leaning to one side since this can put a strain on the SI joint.
- Wear Supportive Shoes: Wear comfortable, supportive shoes that give cushioning and stability. Avoid wearing high heels or shoes with not enough arch support.
- Take Rests and Shift Positions: If standing for lengthy periods, take frequent breaks. One may also consider placing one foot on a footrest or low stool to reduce strain on the SI joint.
Remember to pay close attention to the signals from your body and avoid tasks or circumstances that aggravate SI joint pain. If the pain persists, seeing a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan is best.
How to Sleep With SI Joint Pain
Getting a good night’s sleep might be difficult when suffering from SI joint pain. However, there are certain measures you can use to relieve pain and encourage better sleep:
- Choose the Right Sleeping Position: Choose a sleeping posture that supports the SI joint while minimizing pressure. Laying on your back with a pillow beneath your knees can help keep your spine in place.
- Invest in a Good Pillow: Purchase a pillow that allows for optimal neck and spinal alignment. Memory foam or contoured pillows can help you stay in a neutral position and reduce strain on your SI joint.
- Choose an Appropriate Mattress: Consider a medium-firm mattress that gives you proper support. A too-soft mattress may cause your body to sink, putting additional strain on the SI joint. Test various mattresses and choose one that meets your needs and delivers the most comfort.
6 Best Exercises for SI Joint Pain

SI joint pain can severely impair mobility and quality of life. The SI joint can become dysfunctional or inflamed, causing discomfort and restricted motion. Thankfully, there are workouts designed expressly to relieve this pain. These exercises work by strengthening and stretching the muscles around the SI joint, improving stability, and relieving joint pressure.
Individuals suffering from pain in the sacrum when sitting can find relief, restore mobility, and improve their general well-being by adding these workouts to their daily regimen. To ensure the safety and success of any workout regimen, it is critical to first speak with a healthcare practitioner. Here are some of these exercises.
1. Pelvic Tilts
This exercise involves lying on your back, bending your knees, and gently tilting your pelvis up and down in order to stimulate the core and stabilize the SI joint. Avoid any unexpected jerks by doing this action gently and evenly. Begin with 10 reps and work your way up as tolerated.
2. Knee-To-Chest Stretch
Lie on your back and raise one knee to your chest, holding it with your hands while keeping your other leg straight on the floor. Then hold for 20-30 seconds before alternating legs. This stretch relieves lower back stiffness and stretches the muscles located around the SI joint.
3. Bridge Exercise
Lie on your back, bend your knees, and rest your feet on the floor. Engage your glutes and core muscles to lift your hips off the ground. Hold for a few seconds before descending. Repeat this exercise 10-15 times. The bridge exercise helps strengthen the buttocks and lower back while supporting the SI joint.
4. Piriformis Stretch
Cross one leg over the other knee and slowly move the crossed knee towards the shoulder on the other side until you feel a stretch across your buttocks. Hold for 20-30 seconds before alternating sides. This exercise helps stretch the piriformis muscle, which relieves pressure on the SI joint.
5. Hip Flexor Stretch
Kneel on one knee, keeping the other leg angled at a 90-degree angle in front of you. Stretch your hips forward gently, experiencing a stretch at the front of your hip and thigh. Continue for 20-30 seconds before alternating sides. Stretching the hip flexors might help keep the SI joint balanced.
6. Cat-Camel Stretch
Begin in a tabletop position on your hands and knees. Arch your back like a cat while tucking your lower jaw to your chest, then slide into a curled stance with your buttocks sticking out like a camel. Repeat this action slowly for 10-15 repetitions to enhance SI joint mobility and flexibility.
Treatments for SI Joint Pain
SI joint discomfort develops when the sacroiliac joints connecting the spine to the pelvis become inflamed or dysfunctional. This illness has several possible causes, such as injury, pregnancy, or degenerative changes.
The location of the pain could be in the lower back, buttocks, or hips, producing discomfort and limiting mobility. Non-surgical therapies such as physical therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroid injections are available to treat SI joint pain.
In some circumstances, minimally invasive techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation, could be an option worth exploring. Surgical procedures such as SI joint fusion could be an alternative in more complicated situations. Below are some of the ways in which you can have this condition treated.
Pain Relievers
Pain medications can assist in controlling SI joint pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, naproxen) can successfully reduce inflammation and pain. These drugs act by inhibiting the formation of prostaglandins, which cause pain and inflammation. However, for long-term use or if there are any underlying health conditions, it is critical to adhere to the specified dosage and consult a healthcare practitioner.
These drugs are available over the counter or by prescription. Since some people are allergic to specific prescriptions, make sure these medications will not cause problems based on your medical history.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is essential in the treatment of SI joint pain. A professional physical therapist can create a customized program to strengthen the muscles surrounding the SI joint, improve flexibility, and address any imbalances or postural difficulties. This program may involve core, hip, and pelvic exercises and manual treatment techniques such as joint mobilization or soft tissue manipulation.
Physical therapy seeks to improve stability, realignment, and total function while lowering discomfort and fostering long-term rehabilitation. Physical therapy is a savior for individuals unwilling to take any medication for SI joint pain or if the condition is not too far gone.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive therapy intended to treat chronic SI joint pain unresponsive to conservative treatment. It entails targeting and disrupting the nerves that convey pain signals from the SI joint with heat radiation. A specialized needle containing a heated electrode goes near the afflicted nerves. At this point, the electrode emits radiofrequency energy to produce a lesion, stopping pain impulses.
RFA provides long-term pain alleviation and can significantly enhance function and quality of life in people with SI joint pain. This technique is chosen by those who suffer severely from this condition.
Heat/Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can assist in relieving SI joint pain. This therapy uses a heating pad or a warm bath in the affected area to help enhance blood flow, relax muscles, and alleviate pain and stiffness. Cold therapy, on the other hand, can assist in alleviating inflammation and numb the area, temporarily relieving discomfort.
At the same time, individuals can apply cold or ice packs to the SI joint for short periods. It is essential to use these therapies correctly, avoiding excessive heat or cold exposure to avoid skin harm and adhering to the advice of a healthcare practitioner.
Using Proper Dietary Supplements to Alleviate Joint Discomfort
In case you need supplements for your SI joint discomfort, consider purchasing Joint Support from the experts at PureHealth Research. The product comes in capsule form and contains potent ingredients that can soothe your SI joint. A bottle can cost up to $62, but better offers exist for purchasing more units. You also get two free E-Books with your order once you make a purchase. Sounds enticing, doesn’t it?
These potent natural compounds all work together to improve your overall joint health and well-being by targeting particular joint functions and immune markers. Each has a plethora of scientific research to back up its success. Adults should take two capsules per day since this is one of the dietary supplements for bone and joint health. Take with 6-8 oz of water for optimal benefits or as a healthcare practitioner prescribers.
Anyone suffering from joint stiffness can benefit from this product, which works naturally to promote healthy joints, cartilage, and bone. It also supports flexibility and mobility by regenerating joints and cartilage with specific nutrients.
Moreover, it’s crucial to acknowledge that joint pain from dehydration can exacerbate SI joint discomfort. Staying adequately hydrated ensures that your joints remain lubricated, reducing friction and wear that can lead to pain. This simple yet effective strategy supports overall joint health and can mitigate symptoms associated with SI joint pain.
Final Thoughts
How to sit with SI joint pain can be a tough ordeal. Properly managing SI joint pain requires a multifaceted approach promoting comfort, stability, and self-care. Proper sitting habits, which include maintaining a neutral spine, using supportive cushions and pillows, and avoiding long static positions, can significantly reduce discomfort.
Frequent low-impact exercises to strengthen the core and surrounding muscles will stabilize the SI joint. Also, seeking the advice of a healthcare professional, such as a physiotherapist or a chiropractor, ensures specialized care and exercises. Remember that attentive posture awareness and a proactive commitment to overall wellness help individuals to alleviate SI joint pain and recover the flexibility to enjoy daily activities more comfortably.
Popular Articles
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.