Can Parasites Cause Weight Gain in Humans?
Medically reviewed by our experts


Understanding the intricate ways in which parasites interact with the human body is crucial for maintaining optimal health, prompting many to ask: can parasites cause weight gain?
This question underscores a widespread concern about how these often invisible invaders can impact our well-being in unexpected ways. Common misconceptions about parasites include the belief that they only affect those in specific geographic regions or individuals with certain lifestyle habits.
However, the reality is that parasites may affect anyone, regardless of where they live or how they live their life. This article aims to dispel myths and shed light on the significant impact of parasites on human health, particularly focusing on the relationship between parasites and weight gain.
We will explore how individuals become hosts to parasites, breaking down the various modes of transmission to understand how these organisms may easily infiltrate our lives. Furthermore, we will delve into the symptoms and signs that suggest the presence of parasites, providing readers with essential information on how to recognize potential infestations.
How Do People Get Parasites?
Parasites might infiltrate the human body through a myriad of pathways, highlighting the critical need for heightened awareness and diligent preventive practices. Here is the list of the most common ways how people get parasites:
- Contaminated food and water, where parasites find a direct channel into the host’s system.
- Raw or undercooked meats and unclean fruits. This risk is particularly elevated in regions where water sanitation practices are inadequate.
- Poor personal hygiene, including inadequate handwashing, further exacerbates the risk of parasitic invasions, emphasizing the importance of maintaining cleanliness in daily routines.
- Close contact with infected individuals or animals also serves as a significant vector for transmission, as parasites can easily spread in densely populated or communal living conditions.
- Traveling to areas with high infestation rates dramatically increases the likelihood of encountering parasites, making it essential for travelers to adopt preventive measures such as consuming safe foods and beverages, using protective clothing, and adhering to recommended vaccination schedules.
By understanding these various pathways of entry, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of parasitic infestations through proactive behavior and lifestyle adjustments, safeguarding their health against the unseen threat of parasites.
How to Know if I Have Parasites?

Determining whether you have parasites may be challenging due to the wide range of symptoms they might cause. However, being aware of the most common signs may help you identify a potential parasitic invasion early on. Here’s a concise list of symptoms that may indicate the presence of parasites in your body:
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Persistent digestive issues (e.g., diarrhea, constipation, gas, bloating)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Skin irritations or unexplained rashes
- Sleep disturbances, including night sweats
- Appetite changes, particularly sudden increases
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Allergic reactions without clear causes
- Joint or muscle pain
- Anemia or iron deficiency
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important not to panic but to consider consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and a plan of action. Parasites are a common health issue worldwide, and most infestations can be treated effectively once identified. Awareness and timely action are key to managing the impact of parasites on your health and well-being.
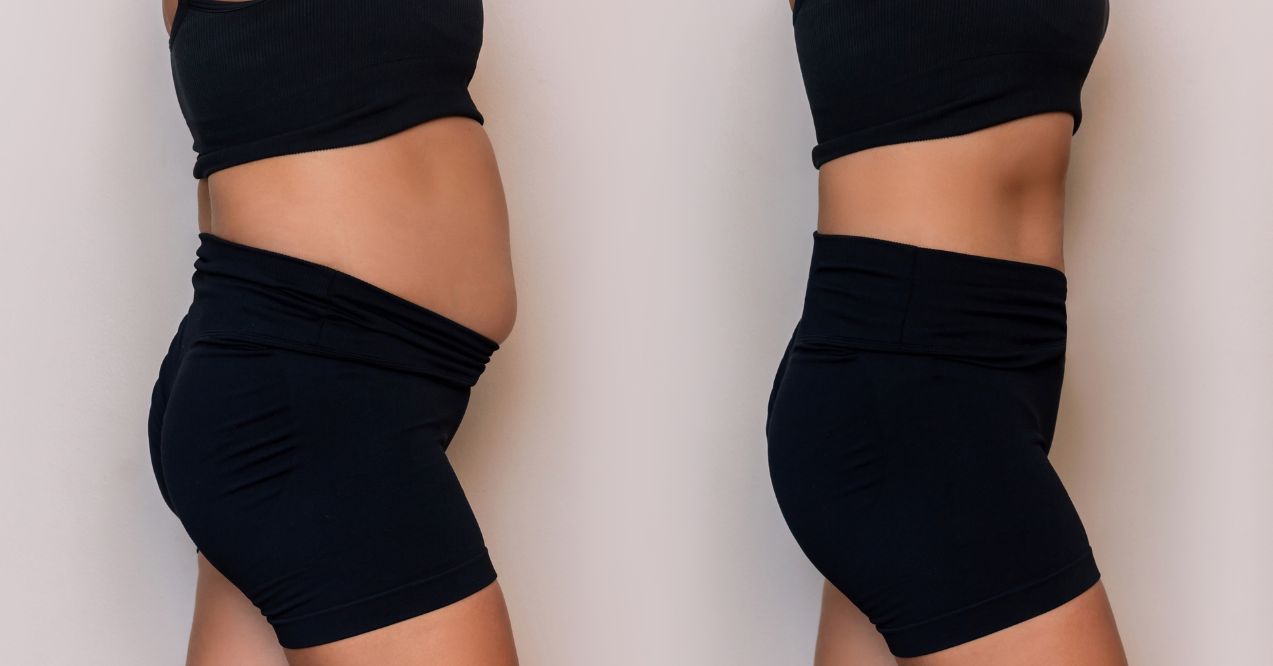
Can Parasites Cause Weight Gain?
The relationship between parasites and weight gain is complex and often misunderstood. While the general perception aligns parasitic infestations with weight loss due to nutrient malabsorption and gastrointestinal distress, it’s important to recognize that certain types of parasites can also contribute to weight gain or impede weight loss efforts.
This counterintuitive effect may arise through various mechanisms, challenging the common narratives surrounding parasites and their impact on human health. So, can parasites cause weight gain?
Inflammation


Firstly, some parasites may trigger pro-inflammatory responses in the body that lead to water retention and bloating, giving the appearance of weight gain or making it difficult to lose weight. The body’s attempt to fight off these invaders can also disrupt normal digestion and absorption processes, leading to an imbalance in gut flora.
This disruption may potentially increase cravings for sugars or carbohydrates, as the parasites feed on these nutrients, leading individuals to consume more calories than usual.
Disrupted Gut


Secondly, the presence of parasites may affect the body’s metabolism and energy levels. Individuals may experience fatigue and a decreased ability to engage in physical activity, reducing the number of calories burned and complicating weight management efforts.
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism and energy homeostasis. When parasites disrupt this delicate balance, they might significantly affect the host’s metabolic rate, possibly leading to an increase in fat storage. This is partly due to the body’s stress response to the invasion, which may trigger the release of cortisol, a hormone that promotes fat storage, especially in the abdominal area.
Furthermore, the altered gut microbiome may impact the regulation of hormones that control appetite and satiety, such as leptin and ghrelin, leading to increased hunger and food intake, further complicating efforts to manage weight.
The stress on the body’s immune system and the overall stress response can further alter metabolism, sometimes leading to an increase in fat storage.
Increased Sugar Cravings


Sugar cravings may intensify significantly when you have parasites, a phenomenon that underscores the complex interplay between these unwelcome guests and your dietary habits. Parasites thrive on the nutrients they extract from the host’s body, with a particular penchant for simple sugars and carbohydrates.
These substances provide the quick energy parasites need to survive, grow, and reproduce within the human body. As parasites consume these sugars, they might stimulate an increase in the host’s cravings for sugary foods and carbohydrates in a bid to replenish their depleted energy reserves.
This cycle creates a challenging situation for the host: the more sugar you consume, the better the environment you create for the parasites to flourish. Consequently, these intensified cravings may not only complicate efforts to manage one’s diet but also strengthen the parasitic stronghold.
Decreased Organ Efficiency


When parasites infest the human body, they can significantly decrease the efficiency of various organs. This deterioration in organ function is due to the parasites consuming nutrients and releasing toxins, which can strain and damage the host’s internal systems.
For instance, liver function may be impaired as it works overtime to filter out the toxins produced by the parasites, leading to pro-inflammatory activity and potentially liver damage over time. Similarly, the kidneys, responsible for filtering waste from the blood and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, can become overburdened by the need to eliminate increased levels of waste and toxins, reducing their efficiency.
Moreover, the presence of parasites may affect the lungs, causing respiratory symptoms and decreasing lung efficiency, especially if the parasite migration includes lung involvement. Parasitic invasions can also impact the heart by increasing the workload due to the body’s heightened effort to circulate blood and nutrients in the face of parasitic demands, leading to potential cardiovascular strain.
How to Avoid Parasites in Humans?
Practice Good Hygiene
Maintaining excellent personal hygiene is a cornerstone in preventing parasitic infestations. Regularly washing your hands with soap and water, especially before eating or after using the bathroom, can significantly reduce the risk of ingesting parasites. It’s also important to keep your living and eating areas clean and free from pests.
Ensure Safe Food and Water Consumption
Consuming safe food and water is crucial. This means drinking water from safe sources or treating it before consumption. When preparing food, wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, cook meat to the recommended temperatures, and avoid raw or undercooked fish and meats.
Avoid Contact with Contaminated Soil or Water
Parasites can live in soil and water, so it’s vital to avoid direct contact with these elements in known contaminated areas. Wearing protective footwear and gloves when gardening or working in soil can help, as well as avoiding swimming in bodies of water that may be contaminated.
Take Preventive Measures When Traveling
When traveling to high-risk areas, take precautions such as consuming only bottled or treated water, avoiding raw foods, and using insect repellent to prevent bites from insects that may carry parasites.
Consume Preventative Supplements
Incorporating preventative supplements into your daily health routine is an effective strategy to bolster your defenses against parasitic infestations. A key component of this preventative approach is understanding how to do a parasite cleanse effectively.
This process typically encompasses dietary adjustments to avoid foods that feed parasites and include those that naturally combat them, alongside adopting enhanced hygiene practices to minimize recurrence risks. The inclusion of specific supplements for cleanse and detox designed to target and help expel parasites from the body is also a critical step.
During a parasite cleanse, it’s not uncommon to experience what is known as parasite die-off symptoms. As the body begins to detoxify, releasing toxins previously harbored by the parasites, individuals might encounter symptoms such as fatigue, digestive discomfort, and flu-like symptoms. These reactions are indicative of the body’s natural process of eliminating toxins and should be seen as a positive sign of recovery.
PureHealth Research Supplements
For those seeking a natural solution to support their fight against parasites, PureHealth Research Parabroom offers a compelling option.
By incorporating this supplement into your daily routine, you can take a proactive step towards alleviating your body of parasites and supporting your digestive health and immune response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, parasites can indeed contribute to weight gain by disrupting the body’s metabolism and causing inflammation. They are transmitted through contaminated food and water, poor hygiene, and contact with infected individuals or animals. Symptoms of parasitic infection can include digestive issues, fatigue, skin irritations, and unexplained weight changes. Preventative measures such as good hygiene, safe food and water practices, and avoiding contaminated environments are crucial. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential for managing potential parasitic infections.
There isn’t a single parasite that’s universally recognized for causing weight gain across all cases. However, some parasites, by affecting the gut microbiome and increasing pro-inflammatory activity, can contribute to weight fluctuation. Parasites can also slow the metabolism and increase cravings for sugar and carbs, indirectly affecting weight management.
Identifying a body full of parasites can involve symptoms such as unexplained weight changes, persistent digestive issues, fatigue, skin irritations, sleep disturbances, appetite fluctuations, abdominal aches, allergic reactions without clear causes, joint or muscle discomfort, and anemia. These symptoms, however, can be indicative of various health conditions, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and solution.
Yes, parasites can significantly change your body by affecting various systems. They can disrupt nutrient absorption, leading to malnutrition or weight gain, alter the gut microbiome, induce pro-inflammatory activity, and cause organ damage or dysfunction. This can manifest in symptoms ranging from digestive issues to changes in energy levels and overall health. It’s crucial to address parasitic infestations promptly to prevent or alleviate these changes.
Popular Articles
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.