How Long Does Parasite Die-off Symptoms Last?
Medically reviewed by our experts


To delve into the question of how long does parasite die-off symptoms last, it’s essential first to understand what parasites are. Parasites are organisms that live on or inside another host organism, deriving nutrients at the host’s expense.
They range from protozoa, like Giardia, to helminths, such as tapeworms, and even ectoparasites, including ticks and lice. Globally, parasitic infections have a significant impact, affecting billions of people. They are particularly prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions but are by no means confined to these areas.
As we explore the journey of sanitizing these infestations, a crucial aspect arises: the die-off symptoms. These occur when the parasites begin to die, releasing toxins into the body, which may cause a range of symptoms. The duration and severity of these symptoms might vary greatly depending on factors like the type of parasite, the individual’s health, and the treatment method used.
This blog post aims to shed light on the typical timeline of die-off symptoms, providing insight into what you may expect during the detoxification process. We will explore the complexities of managing these symptoms and offer guidance to navigate this challenging yet essential phase of recovery. Understanding the nature of parasites and the body’s response to their elimination is pivotal in managing your health and well-being.
Types of Parasites
Parasites, the unwelcome guests in the human body, come in various forms, each with its unique life cycle, diseases, and geographic prevalence. Broadly, they are classified into three main types: protozoa, helminths, and ectoparasites.
1. Protozoa
These are microscopic, single-celled organisms that can be free-living or parasitic. They often multiply within their hosts, leading to serious health issues. A notorious example is Plasmodium, the cause of malaria, transmitted through mosquito bites.
This parasite has a complex life cycle involving both the mosquito and human host, causing symptoms like fever, chills, and anemia. Malaria is predominantly found in tropical regions like sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Another common protozoan is Giardia, which causes gastrointestinal issues and is spread through contaminated water worldwide, including in the United States. The protozoa Blastocystis spp. and Dientamoeba fragilis are isolated mainly in developed countries such as North America, which causes diarrheal illnesses but are rarely tested for this cause.
2. Helminths
These are larger, multicellular organisms commonly known as worms. They include flatworms, such as tapeworms and flukes, and roundworms, like pinworms and hookworms. The most common helminths in America are Ascaris lumbricoides (Ascaris or roundworm), Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm), Necator americanus (hookworm), and Trichuris trichiura (whipworm) contracted through the soil, like gardening. Helminths often live in the gastrointestinal tract but may affect other organs.
For instance, tapeworms, acquired by consuming undercooked meat containing larval cysts, might lead to weight loss and malnutrition. Hookworms, prevalent in regions with poor sanitation, penetrate the skin and eventually reach the intestines, causing anemia and protein deficiency.
3. Ectoparasites
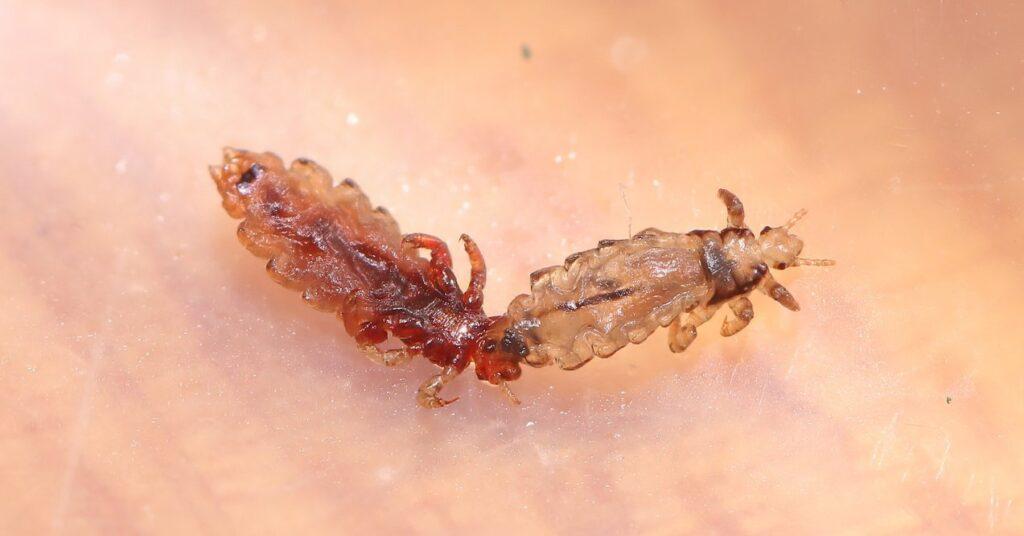

These live on, rather than in, their hosts. They include lice, fleas, ticks, and mites. Ticks, for example, might transmit Lyme disease, causing symptoms ranging from rash to neurological problems, and are prevalent in North America and Europe. Lice infestation, which causes itching and irritation, is a common global issue, especially in crowded living conditions, such as schools.
Each type of parasite has adapted to its environment and host, showcasing the intricate and often disturbing ways nature finds to survive and thrive. Understanding these types and their impacts is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies, especially in regions where they are most prevalent.
Common Ways Parasites Are Transmitted

Parasites have various transmission routes, each as intriguing as it is concerning. Understanding these pathways is key to the management of parasitic infections. Let’s dive into the most common ways parasites find their way into our systems.
- Contaminated Food and Water: This is perhaps the most well-known transmission route. Parasites like tapeworms and Giardia thrive in undercooked meat or contaminated water. For instance, consuming undercooked pork or beef may lead to tapeworm invasions, while drinking water contaminated with Giardia causes gastrointestinal distress. This route is alarmingly common in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene practices, like questionable fast-food joints and kiosks.
- Skin Contact: Some parasites, such as hookworms, have a startling ability to penetrate the skin. Walking barefoot on contaminated soil is a common way to contract hookworms, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Still they may lurk in your backyard, ready to strike while you enjoy the outdoors or gardening. The larvae enter through the skin and travel through the bloodstream to the lungs and intestines.
- Insect Bites: Mosquitoes and ticks are notorious for spreading parasites. The malaria-causing Plasmodium parasite is transmitted through mosquito bites, primarily in regions like sub-Saharan Africa. Ticks might transmit Lyme disease, prevalent in wooded areas of North America and Europe.
- Person-to-Person: Although less common, some parasites may spread directly from person to person. This is often the case with ectoparasites like lice, which spread through close contact or sharing personal items like combs and hats.
- Animals: Close contact with animals may also be a transmission route. Toxoplasmosis, caused by Toxoplasma gondii, might be contracted by handling cat litter, as cats are common carriers.
What Is a Parasite Die-Off?
So, what are die off symptoms of parasites? The die-off, also known as the Herxheimer reaction, occurs when a large number of parasites are killed off in a short period, releasing a burst of toxins into the body. This biological process is fascinating yet may be quite taxing on the body. As the body fights off the parasites, typically through medication or natural defense mechanisms, these organisms release toxins during their demise. It’s akin to a final act of defiance as they break down. This sudden release of toxins might overwhelm the body’s detoxification processes, particularly the liver and kidneys, which are responsible for filtering and eliminating these unwanted substances.
Simultaneously, the immune system kicks into high gear. It recognizes these toxins as foreign invaders, sparking an inflammatory response. This response is the body’s natural way of protecting itself and aids in the healing process. However, it may also lead to a range of symptoms associated with die-off, such as fever, chills, headaches, muscle aches, and fatigue. These symptoms are indicative of the body working hard to cleanse itself.
This die-off process is a testament to the body’s remarkable ability to regenerate and re-establish balance. While it might be uncomfortable, it’s often a sign that the solution is effective and the body is on its way to recovery. Understanding this process is crucial for anyone undergoing treatment for parasitic infestations. It helps in mentally preparing for the journey ahead and underscores the importance of supporting the body through this cleansing phase, whether through hydration, rest, or other supportive therapies. Remember, the discomfort of the die-off is temporary, but the benefits of a body free from parasites are long-lasting.
How Long Does Parasite Die-Off Last?
The duration of die-off symptoms may vary widely among individuals, typically ranging from a few days to a few weeks. This variability is influenced by several factors, including the type and severity of the parasitic infection, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of the cleansing method used. One key factor influencing the duration of die-off symptoms is the body’s ability to detoxify. The more efficient the liver and kidneys are at filtering and eliminating toxins, the shorter the duration of symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and nausea.
Additionally, the type of parasite plays a crucial role; certain parasites may cause more intense die-off symptoms than others. A balanced diet, adequate hydration, and rest might help support the body’s detox processes, potentially reducing the duration and severity of die-off symptoms. It’s also essential to follow the recommended guidelines and dosages for any cleanse protocol to avoid prolonging the die-off phase.
Understanding how to know if parasite cleanse is working may also be helpful. Clear signs include a reduction in original symptoms of parasitic invasion, such as digestive issues, skin irritations, or fatigue. As the body clears out the parasites, there’s often an initial increase in die-off symptoms, followed by a gradual decrease, signaling the effectiveness of the cleanse.
Monitoring the changes in symptoms might provide insights into the effectiveness of the cleanse and the progress of recovery. Remember, patience and adherence to the cleansing protocol are key to navigating this phase successfully.
Common Parasite Die-off Symptoms
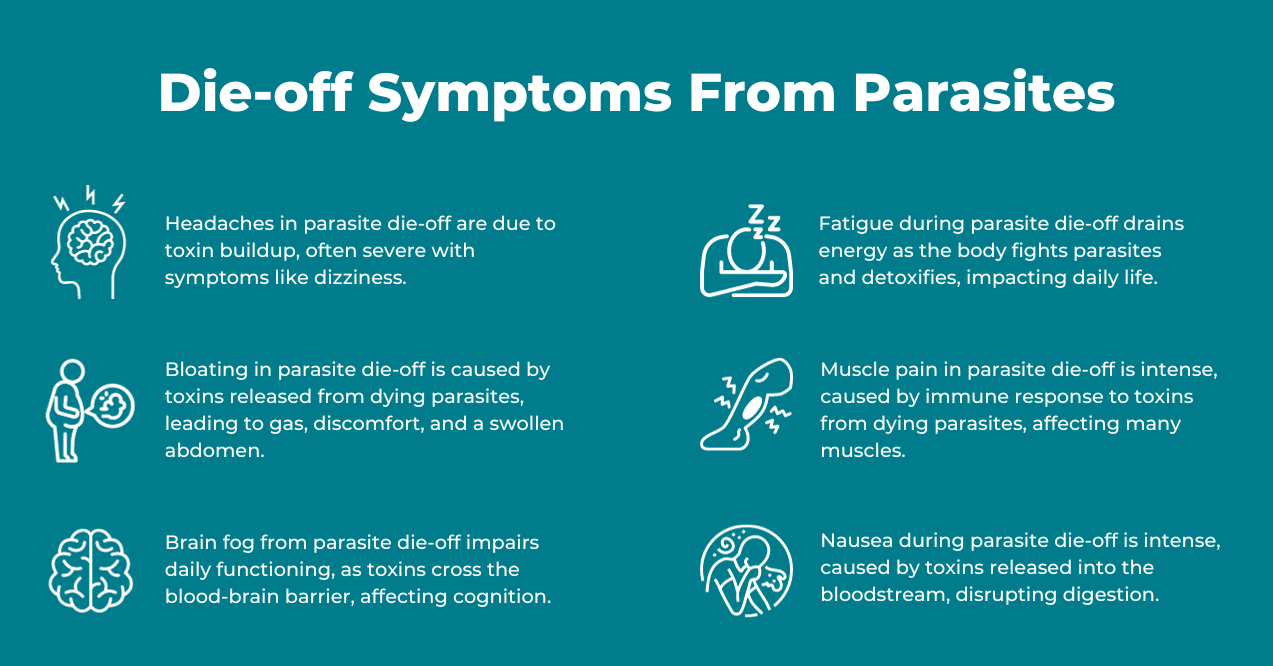
1. Headaches
When delving into the realm of common parasite die off symptoms in humans, headaches emerge as a noteworthy and frequently encountered issue. These headaches are not your typical, everyday headaches; they are often a direct consequence of the body’s rigorous battle against parasites. As parasites die and release toxins, the body’s detoxification systems, primarily the liver and kidneys, work overtime to filter out these harmful substances. This increased workload may lead to a buildup of toxins in the bloodstream, contributing to pro-inflammatory responses and, consequently, headaches.
These headaches may range from mild to severe and are often described as throbbing or pressurizing pains. They might be accompanied by other symptoms like dizziness or light sensitivity, further indicating the body’s intense internal cleansing process.
2. Bloating
Among the myriad of symptoms experienced during the parasite die-off phase, bloating stands out as a particularly common and uncomfortable manifestation. This bloating is not just a typical feeling of fullness; it’s a direct result of the body’s response to the sudden release of toxins as parasites are being eliminated. As these unwelcome organisms perish, they release substances that may disrupt the normal balance of gut flora and irritate the gastrointestinal tract.
This disturbance often leads to an increase in gas production and a sensation of swelling in the abdomen, contributing to a feeling of tightness and discomfort. Bloating during a parasite die-off might also be exacerbated by the body’s heightened immune response, which is part of its natural defense mechanism against the flood of toxins. It’s important for individuals experiencing this symptom to understand that bloating is a temporary, albeit distressing, part of the recovery process, and strategies like maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and gentle exercise may help alleviate this discomfort.
3. Brain Fog
Brain fog is particularly notable as one of the die off symptoms from parasites, often overshadowing other physical discomforts. This cognitive cloudiness emerges not just as a mild inconvenience but as a significant impediment to daily functioning. As the body works to expel parasites, the release of toxins may disrupt normal brain function. These toxins may cross the blood-brain barrier, a protective shield meant to keep harmful substances out of the brain. When this barrier is compromised, it may lead to a decrease in cognitive function, manifesting as brain fog.
Those experiencing brain fog during die-off might find themselves struggling with memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, or a general sense of mental sluggishness. This symptom underscores the interconnectedness of physical and mental health during the detoxification process. It’s a temporary but impactful sign that the body is undergoing a profound internal cleanse, working to regain optimal function.
4. Fatigue
Fatigue, a common and often debilitating symptom experienced during the parasite die-off phase, significantly impacts daily life. This profound sense of tiredness and lack of energy goes beyond normal exhaustion. It occurs as the body expends considerable effort in fighting off and expelling parasites. As these parasites die, they release a surge of toxins into the system.
The body’s natural response is to ramp up its detoxification processes, particularly in the liver and kidneys, to filter out these harmful substances. This heightened state of internal activity demands substantial energy, diverting resources that would normally be used for everyday activities, leading to a pervasive feeling of fatigue. Additionally, the immune system’s response to the die-off may also contribute to this exhaustion.
5. Muscle Pain
Muscle pain is a notable and often distressing symptom commonly encountered during the parasite die-off process. This particular discomfort goes beyond ordinary muscle soreness; it’s a direct consequence of the body’s intense internal struggle against parasitic invaders. As parasites die and release toxins, the body’s immune system is activated to an extraordinary degree, leading to widespread immune activation.
This proinflammatory response, while a natural and necessary part of the recovery process, may cause muscle tissues to swell and become painful. The pain might range from a dull, constant ache to sharp, sporadic spasms, affecting various muscle groups. The intensity of the muscle pain often correlates with the severity and extent of the parasitic infection, as well as the body’s efficiency in eliminating the toxins.
6. Nausea
Nausea, a frequent and often challenging symptom, emerges prominently during the parasite die-off phase. This feeling of unease and discomfort in the stomach is more than just a typical upset; it’s a direct response to the body’s intense cleansing process. When parasites are being eliminated, they release a variety of toxins into the bloodstream.
The body, in its effort to detoxify itself, may sometimes become overwhelmed by this sudden influx of harmful substances, leading to a disruption in the normal functioning of the digestive system. This disruption often manifests as nausea, a natural reaction to the perceived internal threat. The severity of nausea may vary, sometimes accompanied by an aversion to food and a general sense of abdominal discomfort.
Parasite Cleanse Side Effects
Embarking on a parasite cleanse may be a transformative journey towards better health, but it’s crucial to be aware of the potential side effects and the importance of medical supervision. A parasite cleanse, typically involving herbal supplements or prescribed medications, aims to rid the body of parasitic infections. However, this process is not without its risks and parasite cleanse side effects.
Firstly, as parasites die off, they release toxins into the body, which may lead to a range of symptoms like nausea, headaches, fatigue, and digestive disturbances. This phenomenon, often referred to as the Herxheimer reaction, occurs because the body’s detoxification pathways, primarily the liver and kidneys, might become overloaded with these toxins. The severity of these side effects may vary depending on the type and number of parasites present, the strength of the individual’s immune system, and the effectiveness of their detox pathways.
Another potential risk is an allergic or adverse reaction to the ingredients in herbal cleanse products. Not all natural remedies are safe for everyone, and some may interact with existing medications or medical conditions. It’s also possible to overdo it, leading to more severe symptoms like dehydration, nutrient imbalances, or even organ damage in extreme cases.
This is why medical supervision is vital during a parasite cleanse. A healthcare professional might help ensure the cleanse is necessary and safe, tailor the treatment to the individual’s specific needs, and monitor for any adverse reactions or complications. They may also provide guidance on supporting the body through the detox process, such as staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and getting adequate rest.
How to Reduce the Effects of Specific Die-Off Symptoms
Managing the effects of parasite die-off symptoms effectively involves a combination of lifestyle and dietary strategies. How to do a parasite cleanse that would be successful? A balanced diet with whole foods, fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, lean grass-fed beef, pasture-fed poultry, wild-caught fish, fiber, and probiotics helps maintain a healthy digestive system, crucial for eliminating toxins released during die-off. For those with digestive disorders or a leaky gut, avoiding dairy, fiber, and probiotics is best until your gut achieves balance.
Hydration cannot be overstated in its importance. Drinking plenty of water facilitates the kidneys and liver in filtering and flushing out toxins. Herbal teas, particularly those with detoxifying properties like dandelion or milk thistle, might also be beneficial. It’s essential to avoid dehydration, as it may exacerbate symptoms like headaches and fatigue.
Rest is another crucial component. The body undergoes significant stress during a die-off, and adequate sleep provides an opportunity for recovery and rejuvenation. It’s during rest that the body can repair itself and strengthen the immune system, which is essential for fighting off parasites and dealing with the influx of toxins.
Understanding the symptoms and taking proactive steps to mitigate them can make the parasite cleanse journey more bearable. For instance, if you experience muscle pain, gentle stretching or warm baths may provide relief. If bloating or digestive issues arise, eating smaller, more frequent meals can help. For brain fog, activities that stimulate mental clarity, like light exercise or brain games, might be beneficial.
Natural supplements can also play a significant role in this holistic approach. PureHealth Research’s Parabroom is an example of an all-natural supplement that has gained attention for its potential benefits in supporting overall well-being.

Endorsed by health experts like Dr. Holly, Parabroom is formulated to assist the body’s detoxification processes. Its natural ingredients are selected to help ease the burden of eliminating toxins, potentially making the die-off process more manageable.
How to Prevent Parasite Die-off Symptoms?
To prevent parasite die-off symptoms, it’s essential to adopt strategies that minimize the risk of parasitic infestations and prepare the body for a potential cleanse. Good hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing before eating and after using the restroom, are crucial in avoiding the spread of parasites.
Safe food handling, taking extra care to eliminate parasites when washing fruits and vegetables you intend on eating raw, and proper cooking techniques and temperatures may also significantly reduce the risk of ingesting parasites. If you’re planning to start a cleanse, preparing your body in advance might help mitigate the intensity of parasite die-off symptoms.
Ensuring adequate hydration is essential to facilitate toxin elimination. People with digestive disorders, such as IBD, IBS, SIBO, or a leaky gut, should avoid processed foods, sugars, starchy carbs, artificial sweeteners, high-fiber foods, dairy, and probiotics. You can prepare by focusing on whole foods, raw or cooked fruits and vegetables as tolerated, grass-fed/pasture-fed lean protein, wild-caught fish, and nut and seed butter. For those without GI disorders, you can prepare by optimizing your diet with fiber-rich foods and probiotics to support gut health and avoid sugars and starchy carbs. Gradually introducing detoxifying foods, like garlic and turmeric, may also help strengthen your body’s natural detox pathways.
Additionally, maintaining a balanced lifestyle with adequate sleep and stress management techniques might support your immune system.
Key Takeaways
Embarking on a parasite cleanse involves understanding and managing die-off symptoms, which occur when the body eliminates parasites, releasing toxins. These symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Bloating
- Brain fog
- Fatigue
- Nausea
How long should you parasite cleanse? They vary in duration, typically lasting from a few days to a few weeks, depending on factors like the individual’s health and the type of parasite.
To mitigate these symptoms, a holistic approach involving:
- Balanced diet
- Hydration
- Rest
- Natural supplements like Parabroom.
Prior to starting a cleanse, adopting preventative measures against parasitic invasions, such as good hygiene practices and safe food handling, is crucial.
Preparing the body with a nutrient-rich diet and probiotics may also ease the intensity of die-off symptoms. Monitoring changes in symptoms might provide insights into the effectiveness of the cleanse. Overall, patience and adherence to a well-planned cleanse protocol are essential for a successful and comfortable detoxification process.
A parasite cleanse can lead to side effects, commonly known as die-off symptoms, including headaches, nausea, fatigue, bloating, and brain fog. These occur as the body reacts to the release of toxins from dying parasites. The severity and duration of these symptoms vary based on individual health and the type of parasites involved.
Parasites are commonly transmitted through contaminated food and water, skin contact with affected surfaces, insect bites (like mosquitoes and ticks), direct person-to-person contact, and exposure to animals with parasites, especially in areas with poor sanitation, but can be anywhere.
Popular Articles
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.