How Does Alcohol Affect the Central Nervous System?
How does alcohol affect the central nervous system is a question many have pondered. Check our article to learn more about its short-term and long-term effects.


The central nervous system (CNS) plays a pivotal role in our body’s function, and the impact of alcohol on the CNS can be profound. Whether you enjoy an occasional drink or frequently partake, understanding how alcohol affects the central nervous system is essential.
Over the ages, alcohol has become synonymous with relaxation, celebrations, and social engagements. Its historical relevance and cultural significance cannot be overlooked. However, the flip side of this widely consumed psychoactive substance reveals startling effects on our health, especially the CNS.
The spectrum of alcohol’s impact on the nervous system is vast. It ranges from subtle changes in mood and cognition after a single drink to irreversible brain damage with chronic, excessive consumption. In this article, we delve into the nuances of how alcohol affects the central nervous system in the short term and its long-term consequences.
The toll of alcohol abuse is not just social or economic; it’s deeply physiological. Understanding these effects provides insight into the behavioral shifts one may experience and underscores the importance of moderation. Ready to discover the intricate relationship between alcohol and the CNS? Dive in.
What Is the Nervous System?
Before diving deep into the impact of alcohol on the central nervous system, it’s pivotal to have a grasp of what the nervous system entails. Essentially, the nervous system is an intricate network composed of nerve cells and their pathways, responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body. Let’s break down its major components:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Acting as the primary control center, the CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. These vital components are safeguarded by the skull and spine, ensuring they remain unharmed.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): This system encompasses the vast web of nerves branching out from the CNS, spanning the entirety of the body.
- Autonomic Nervous System: Operating largely without conscious intervention, this system regulates vital involuntary processes like blood pressure, heartbeat, and digestion. It coordinates a complex network including internal organs, blood vessels, and glands involved in sweat and saliva production.
- Motor Nerves: Originating in the spinal column and culminating in specific muscles, these nerves are pivotal for movement. They’re categorized as:
- Somatic – Governing skeletal muscles.
- Special Visceral – Overseeing facial and neck muscles.
- General Visceral – Managing smooth muscles, such as those found in the heart.
Alcohol’s deleterious effects on these nerves can manifest as muscle cramps, weakness, and even functional loss.
- Sensory Nervous System: This subsystem is made up of sensory receptors which relay signals from organs back to the brain and spinal cord. Alcohol-induced damage to these nerves might result in symptoms like numbness, pins-and-needles sensations, and tingling.
The Detrimental Health Impact of Alcohol Abuse
Excessive alcohol consumption isn’t just about the immediate hangovers or short-lived euphoria. The long-term health implications, especially on the central nervous system (CNS), are far-reaching and often underestimated.
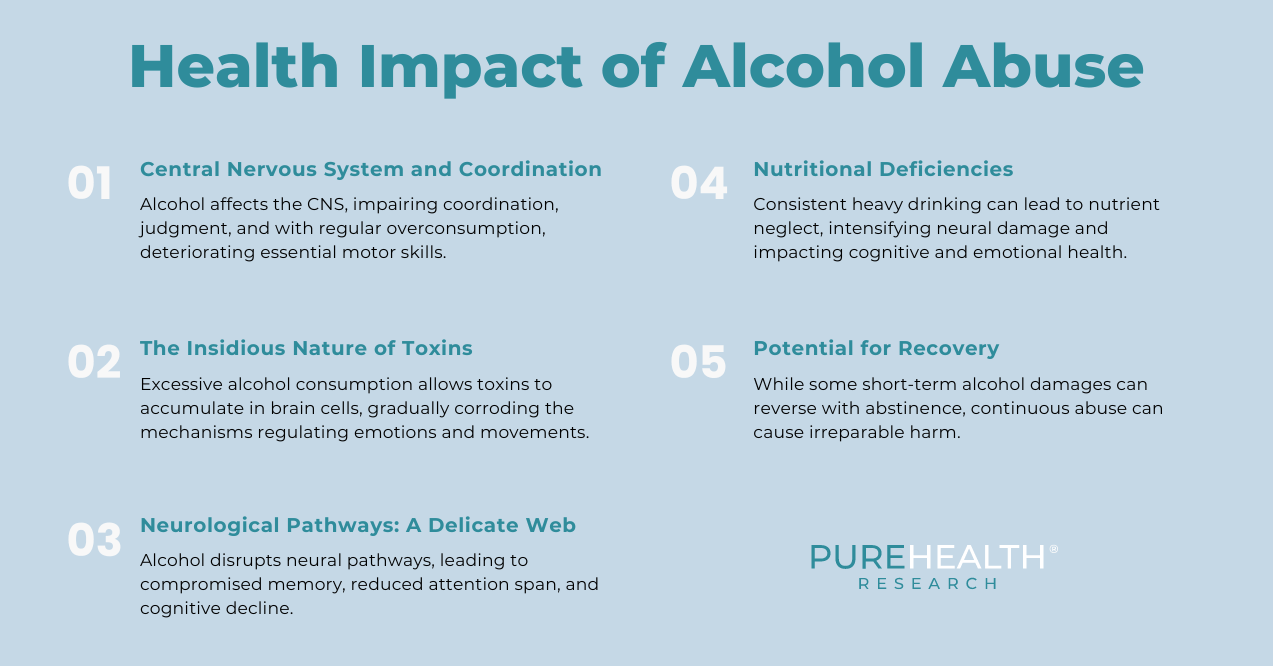
Central Nervous System and Coordination
When you drink alcohol, your CNS takes a hit. Alcohol impedes coordination, slows reaction time, and clouds judgment. This isn’t just a transient state; regular overconsumption can deteriorate essential motor skills, affecting balance, agility, and even speech.
The Insidious Nature of Toxins
Here’s something to ponder: each time you indulge beyond moderation, toxins from the alcohol seep into your cells. Over time, these toxins accumulate, especially in the brain cells that regulate emotions and movements. Think of it as a corrosion process, silently and steadily wearing out the brain’s complex machinery.
Neurological Pathways: A Delicate Web
Alcohol doesn’t stop cell damage. It sneaks into intricate neural pathways, causing disruptions in communication between different brain regions. Result? A compromised memory shortened attention span, and general cognitive decline.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Consistent heavy drinking often accompanies neglect of essential nutrients, particularly thiamine. The deficiency of such vital vitamins can exacerbate the neural damage caused by alcohol, affecting cognitive functions and emotional health.
Potential for Recovery
It’s not all doom and gloom. Some of the short-term damages from alcohol can reverse with abstinence. But, and it’s a significant “but,” continuous abuse without intervention can lead to irreparable harm.
Your health isn’t a game of roulette. Every choice has consequences. By understanding these consequences and staying informed, you can make decisions that prioritize your well-being.
How Does Alcohol Affect the Central Nervous System? Impact and Risks
Alcohol doesn’t just quench thirst or lighten the mood. It launches a cascade of effects, particularly on the CNS, with implications that might surprise many.
When you sip that glass of wine or beer, the alcohol doesn’t linger in your stomach. Rapidly entering the bloodstream, it makes its way to various organs, most notably the brain. Here, it doesn’t just sit idly; it influences the CNS pathways, shaping the way you feel, think, move, and even perceive the world.
Factors Influencing Alcohol’s Effect on CNS
Alcohol’s impact on your CNS isn’t uniform; it varies based on:
- Frequency of Consumption: How often do you drink?
- Quantity: How much do you imbibe in a session?
- Quality: Is it a high-quality spirit or a cheap blend?
- Onset of Drinking: At what age did you start?
- Personal Factors: Gender and weight play a role.
- Combination: Mixing alcohol with drugs or other substances escalates the risks.
Alcoholic Neuropathy
Prolonged excessive drinking can give rise to alcoholic neuropathy – a sophisticated term for nerve damage primarily affecting the peripheral nervous system. This isn’t just a vague medical term; its symptoms can be painfully real:
- Sensations of numbness and tingling.
- Issues related to male potency.
- Urination and bladder irregularities.
- Muscle cramps and weakness.
- Pain, ranging from the feet to the hands.
- Digestive problems, including diarrhea and constipation.
- Sensitivity issues to extreme temperatures.
Neuropathy isn’t an overnight phenomenon; it builds over time. The silver lining? By cutting back or quitting alcohol, you can halt its progression. But be warned, restoring already lost nerve function is a challenge, if not impossible.
How Does Alcohol Affect the Central Nervous System in the Short Term?
The immediate impact of alcohol on your CNS can be pronounced. While alcohol’s influence spans both short and long durations, this section focuses on the immediate or short-term repercussions.
- Headache: Alcohol acts as a diuretic, leading to increased urine production and potential dehydration. The imbalance of fluid levels and electrolytes can be a direct trigger for headaches, often causing individuals to reach for painkillers the next morning.
- Inability to Balance: The cerebellum, responsible for coordination and movement, is impacted by alcohol consumption. As a CNS depressant, alcohol slows the brain-body signal transmission, resulting in compromised coordination.
- Slurred Speech: The prefrontal cortex, vital for speech production, gets affected by alcohol. The disruption in neurotransmitters that coordinate muscle movements results in unclear pronunciation and slurred words.
- Blackouts: A high alcohol concentration can hinder the hippocampus, essential for memory formation. This impairment in memory consolidation leads to gaps in recollection, sometimes causing complete memory blackouts.
- Difficulty in Concentration: Alcohol influences the lobe responsible for attention, decision-making, and focus. Additionally, disrupted neurotransmitter systems affect information processing, challenging one’s ability to maintain mental acuity.
It’s essential to be aware of these short-term effects to make informed decisions about alcohol consumption. The brain is a delicate organ, and even brief exposures to depressants like alcohol can have noticeable consequences.
Alcohol’s Long-Term Impact on the Nervous System

While many people focus on the immediate effects of alcohol, its long-term repercussions on the nervous system can be profound and damaging. Here’s a closer look at the sustained damage caused by chronic alcohol consumption:
- Mental Health Decline: It’s a tragic irony that many turn to alcohol to alleviate feelings of depression or anxiety, only to find these symptoms aggravated in the long run. The reason? Alcohol disrupts the brain’s delicate balance of neurotransmitters, often intensifying depressive symptoms and heightening anxiety. This can create a vicious cycle of drinking as an ill-advised remedy for the very problems it exacerbates.
- Sexual Dysfunction: The repercussions of consistent alcohol consumption on sexual health are often underestimated. In men, alcohol disrupts nerve pathways crucial for achieving and maintaining erections. Additionally, it can diminish testosterone levels, further complicating matters. Women aren’t spared either; they might notice a decrease in sexual desire and responsiveness, as alcohol hinders the nervous system’s ability to relay sexual stimuli.
- Sleep Disruption: A common misconception is that alcohol aids sleep. While it might induce drowsiness initially, it often jeopardizes sleep quality. By disrupting the natural sleep cycle, alcohol can lead to frequent awakenings and reduced restorative sleep, which in turn causes daytime fatigue and cognitive impairments.
- Temperature Dysregulation: Chronic alcohol misuse can impair the body’s temperature regulation mechanism. Though it’s not unusual to feel warmer or cooler when drinking, consistent overconsumption can disrupt the body’s thermal balance, leading to excessive sweating or chills. This not only affects personal comfort but also heightens the risk of conditions like hypothermia or heat stroke in extreme temperatures.
- Diminished Focus: Over time, alcohol can degrade certain areas of the brain responsible for attention and focus. This results in compromised concentration, memory retention, and multitasking abilities. The diminished cognitive function can obstruct personal and professional accomplishments, affecting various life facets.
In conclusion, while the immediate effects of alcohol might be fleeting, its long-term consequences can linger, affecting the quality of life in multifaceted ways. Being informed about these impacts is essential for making informed decisions about alcohol consumption.
Supplements Can Be a Helpful Way to Recover!
Key Ingredients & Their Benefits:
- R-Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Shields nerve cells from stress and promotes nerve health.
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine: Boosts nerve cell energy and supports nerve regeneration.
- B Vitamins (B3, B6, B12): Ensures optimal communication and repair of nerve cells.
- Baical Skullcap Root Extract: Calms the system, benefiting nerve function.
- Passionflower Extract: Reduces nerve-associated tension and discomfort.
- Oat Straw Extracts: Soothes the nervous system, preventing jittery feelings.
- Riboflavin: Enhances B vitamin absorption, crucial for the nervous system.
Why Choose Nerve ReGen Formula by PureHealth Research?
- Research-Backed: Ingredients are chosen based on scientific evidence.
- Purity Guaranteed: No additives, fillers, or artificial preservatives. Crafted in a certified facility.
- Easy Incorporation: Simply fit it into your daily routine for nerve care.
Benefits You Can Expect:
- Rebuild and repair the myelin sheath.
- Restore cellular nutrients and increase signal speed.
- Alleviate symptoms of nerve dysfunction.
- Calm nerves, soothe discomfort and promote sleep.
- Protect against specific nerve-related issues and enhance nerve functions.
While this formula aims for the utmost safety, if you’re on antacids, calcium-based heart medication, chloramphenicol, or liver-processed drugs, consult your physician. Pregnant individuals should consult with the doctor before using the formula. For those seeking overall wellness, this product can complement other supplements for nervous system, supporting a holistic approach to your health.
Final Thoughts
The implications of alcohol consumption, both in the short and long term, are profound. While moderation or abstinence is the best preventive course, remember that if you’ve already faced some of the repercussions, it’s never too late to make positive changes.
Equipped with knowledge about the severe effects of excessive drinking, it’s essential to take proactive steps now. Prioritize your well-being and start your journey towards a healthier future today.
In the short term, alcohol can impair coordination, cause slurred speech, lead to memory blackouts, induce headaches, and make it difficult to concentrate. These effects occur because alcohol disrupts the brain’s communication pathways, affecting areas responsible for movement, speech, memory, and attention.
Long-term alcohol consumption can lead to neurological damage, mental health decline, sexual dysfunction, sleep disruption, temperature regulation issues, and diminished cognitive function. Chronic alcohol abuse can cause irreversible damage to the brain and nerves, significantly impacting overall health and quality of life.
Yes, chronic alcohol abuse can cause permanent damage to the nervous system. This includes conditions like alcoholic neuropathy, where peripheral nerves are damaged, leading to numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. Prolonged alcohol use can also result in lasting cognitive impairments and mental health issues.
Several factors influence alcohol’s impact on the central nervous system, including the frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption, the quality of the alcohol, the age at which one started drinking, personal factors like gender and weight, and the combination of alcohol with other substances or medications.
While some short-term effects of alcohol on the nervous system can be reversed with abstinence, long-term damage may be more challenging to repair. Recovery can be supported by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, consuming a balanced diet, and using supplements designed to promote nerve health, such as those containing R-Alpha-Lipoic Acid, B Vitamins, and Acetyl-L-Carnitine.
Sign up for our Healthy Living newsletter!
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.