Can Obesity Cause Shortness of Breath? Exploring the Link
Medically reviewed by our experts


With obesity rates skyrocketing across the globe, one question looms large: can obesity cause shortness of breath? Astoundingly, over the past three decades, countries worldwide have witnessed obesity rates double or even triple. Urban sprawl, sedentary screen-time, and the allure of calorie-packed processed foods are key culprits.
Obesity wears many faces. While most recognize its notorious associates like diabetes, affecting a staggering 422 million globally, or heart diseases, there’s a silent, lurking symptom: breathlessness. It’s not just about feeling a tad winded. For many, it’s a heart-pounding, suffocating sensation.
Breathlessness, technically termed dyspnea, signifies the distressing feeling of oxygen deprivation. Its effects on well-being are profound, oscillating between mild unease to an outright feeling of asphyxiation. And though numerous culprits might leave you gasping, recent research indicates obesity as a prime suspect.
To the burning question, does obesity cause shortness of breath? — the verdict is a yes. But understanding this relationship between the two is pivotal. In this piece, we’ll unravel the complex web between obesity and shortness of breath, exploring the root causes and diving deep into tangible remedies. Together, we’ll chart a path to reclaiming not just your breath, but your health.
What Is Morbid Obesity?
Morbid obesity isn’t just a term; it’s a heartfelt concern for many. If you or a loved one finds themselves within this category, know you’re not alone and that understanding is the first step to transformation. When an individual’s body mass index (BMI) surpasses 30 and comes with other health challenges, they’re often termed as morbidly obese. This isn’t about judging or labeling, but about comprehending the depth of the issue.
Our world is complex, and so is our health. The World Health Organization (WHO) gives us a perspective on obesity, breaking it down through the lens of BMI. But it’s more than just a number. Factors like waist-hip ratio and cardiovascular risk variables all play pivotal roles in understanding our health.
For children, the definition of a ‘healthy’ weight varies with age and gender. Historical comparisons often set the benchmark. Let’s simplify this understanding:
- Class 1: BMI between 30 and 35
- Class 2: BMI between 35 and 40
- Class 3: Often referred to as ‘severe’ obesity, this involves a BMI of 40 or above.
Now, to a pressing question: Does morbid obesity affect one’s breathing? In short, yes. Breathlessness is more than just a physical strain; it’s a silent echo of the challenges the body faces internally. One such condition is obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS), a distressing respiratory challenge that sees reduced oxygen levels in the blood and increased carbon dioxide levels.
Extra fat around vital areas, hormonal imbalances, or even neurological challenges can inhibit optimal respiratory function. Left unchecked, this may pave the way to grave health challenges. Yet, with understanding comes empowerment. Recognizing the issue means you’re one step closer to crafting a healthier tomorrow.
What Are the Main Causes of Obesity?

Obesity is more than just a term; it’s a complex interplay of various factors that culminate in increased body fat, possibly impacting our health. While it’s crucial to understand that having surplus body fat isn’t a disease, when it crosses a certain threshold, it can subtly alter our body’s internal dynamics. These shifts are progressive and may escalate, posing potential health risks.
By delving deep into the catalysts of obesity, we can better understand the diverse experiences and susceptibilities of individuals. Here’s a closer look at the primary drivers:
- Dietary Choices: Consuming foods high in fats and sugars can quickly pack on the pounds, especially if they aren’t counteracted with adequate physical activity. Remember, a calorie unburned is a calorie stored.
- Medical Conditions: Some conditions, like hypothyroidism or polycystic ovarian syndrome (POS), can skew the body’s weight regulation mechanisms, making weight gain more prevalent.
- Genetics: Our DNA can play a role in our propensity towards weight gain. Although certain genes can influence metabolism and weight management, they don’t seal our fate. External factors like diet and exercise remain paramount in shaping our health trajectory.
- The Power of Rest: There’s more to sleep than just recharging. Insufficient or fragmented sleep can toy with our appetite hormones, intensifying hunger and tempting us towards overindulgence. Moreover, it might alter our energy usage, increasing the chances of calorie accumulation.
- Stress’s Silent Toll: In an age of perennial rush, stress has become a silent companion. Persistent stress releases cortisol, which, in turn, can lead us to seek high-calorie comfort foods. This makes maintaining a balanced weight more challenging, especially when stress begins dictating our lifestyle choices.
By grasping these influencers, we’re not only educating ourselves but also taking the first step towards a healthier, more informed life journey.
Can Obesity Cause Shortness of Breath?

If you are still wondering, “Can obese belly fat cause shortness of breath?” It sure can! Obesity directly impacts how your lungs function through physiological mechanisms. There are two patterns of weight gain: central obesity and peripheral obesity. Weight gain in the chest and abdomen, which gives the body the “apple shape,” results in central obesity. Because the body usually stores fat around the hips, thighs, and limbs in peripheral obesity, this body type is known as “pear-shaped.”
Breathlessness may come with central fat accumulation in obese people. Excess body fat in the chest and belly might limit lung expansion even at rest, changing your typical breathing rhythm and causing you to breathe more shallowly.
Let’s look at the various ways that obesity might lead to respiratory problems.
- Excess Body Fat: Deep breathing can become more difficult due to a surplus of body fat, especially in the belly, chest, and neck areas, limiting lung expansion and constricting the chest cavity. People may have shortness of breath as a result, especially while physically active or, in rare circumstances, even when at rest.
- Reduced Lung Function: Obesity can impair lung function by diminishing lung compliance and the effectiveness of the respiratory muscles. The primary breathing muscle, the diaphragm, may weaken and lose part of its efficiency in obese individuals. Additionally, being overweight might result in airway inflammation and anatomical changes that worsen lung function.
- Sleep Apnea: A common respiratory disorder called sleep apnea has the defining characteristic of breathing pauses while you’re asleep. During sleep apnea, it is common for your airways to become partially or totally blocked while asleep. The breathing pauses that occur often cause frequent awakenings and sleep pattern disturbances.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: If your heart isn’t circulating enough oxygen-rich blood, your body will attempt to obtain more oxygen by forcing you to breathe more quickly, making you feel out of breath.
- Reduced Physical Activity Tolerance: Exercise can be physically stressful for obese people due to their additional weight. Even simple actions like walking a short distance or climbing stairs might leave you fatigued and out of breath. The greater energy expenditure needed and the restrictions put on the body by the excess weight are the main causes of the decreased capacity for exercise.
Obesity-related shortness of breath can appear during physical activity and rest, especially in those with severe obesity or underlying respiratory problems. Can obesity cause shortness of breath while lying down? Due to the strain the weight of the belly puts on the lungs, resting flat may make obesity-related shortness of breath worse.
Is Shortness of Breath Normal?

Shortness of breath can happen due to various circumstances and, depending on the setting, may be normal or pathological. It can occasionally manifest as a physiological reaction to physical effort or specific emotions. However, contact an ambulance or arrange for someone to quickly transport you to the emergency room if your shortness of breath is so severe that it interferes with your ability to perform your normal daily activities.
People with shortness of breath may experience airway narrowing or constriction when engaging in strenuous physical exercise. It results in wheezing, coughing, and other symptoms during or after exercise. Most patients with these exercise-induced symptoms may be able to keep up their activity levels and exercise with proper treatment.
On the other hand, if shortness of breath continues during even little exertion, even at rest, or interferes with daily activities, it may be an indication of an underlying medical condition. Several reasons, including bronchial asthma, congestive heart failure, interstitial lung disease, and pneumonia, typically result in chronic dyspnea.
Solutions for Easier Breathing
Several techniques and lifestyle adjustments can assist in improving your breathing and overall respiratory function if you frequently feel out of breath. Here are some suggestions to help you improve your breathing:
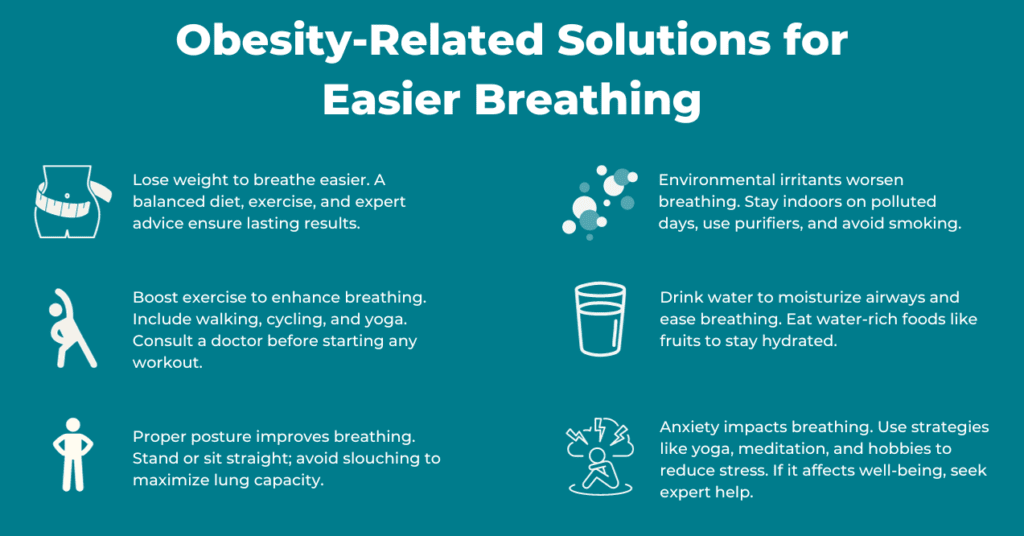
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Lowering your weight can help your breathing and reduce the strain on your respiratory system. Following a healthy, balanced diet, working out often, and getting professional advice may create a safe and long-lasting weight loss strategy.
- Regular Exercise: Increasing physical activity can strengthen your breathing muscles. You’ll experience less difficulty breathing when doing daily tasks as a result. Incorporate activities like walking, cycling, swimming, and yoga into your routine. Start slowly and move forward at a rate that suits your fitness level. Before beginning any new workout regimen, get medical advice. It’s always wise to consult with your doctor before starting any exercise program.
- Maintain Good Posture: A proper posture can help the lungs expand to make breathing easier. Ensure you maintain good posture by standing or sitting up straight with your shoulders pulled back and your spine in proper alignment. Avoid hunching over or slouching since this might limit lung expansion.
- Avoid Exposure to Airborne Irritants: Environmental elements, including smoke, dust, air pollution, and strong chemical scents, can exacerbate respiratory problems. Staying inside on days with poor air quality, using air purifiers, and avoiding smoking are all ways to reduce exposure to these irritants.
- Keep Hydrated: Drinking adequate amounts of water keeps the airways moist and helps thin mucus production, making breathing easier. Drink plenty of water and consume meals that are high in water, such as fruits and vegetables, to prevent dehydration.
- Manage Stress: Anxiety and stress can affect respiratory patterns and make it harder to breathe. Use stress-reduction strategies, including yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and engaging in relaxing hobbies and pursuits. If stress and anxiety are adversely impacting your well-being, get expert assistance.
Always seek individualized advice and treatment choices tailored to your condition from a healthcare expert. They can advise you on the best methods to treat your unique breathing issues and enhance your overall respiratory function.
Final Thoughts
So, can obesity cause shortness of breath? It’s only natural that you will find breathing more difficult since this condition strains your respiratory system more. People who are overweight may have difficulty breathing due to increased chest cavity pressure and reduced lung function, particularly while exercising or, in extreme cases, even when at rest. Recognizing the correlation between obesity and respiratory issues is critical for raising risk awareness and empowering people to make positive lifestyle changes.
Enhance your respiratory function and lessen shortness of breath by keeping a healthy weight, exercising often, using the right breathing methods, and taking care of underlying health issues. For individualized guidance and treatment choices, speaking with healthcare specialists is crucial. Such an approach will improve your general well-being and quality of life.
Yes, obesity can cause shortness of breath. Excess body fat, particularly around the chest and abdomen, can limit lung expansion and reduce lung function, leading to difficulty in breathing. This condition is often referred to as dyspnea.
Obesity is caused by a combination of factors including poor dietary choices, medical conditions like hypothyroidism, genetic predisposition, lack of sleep, and chronic stress. These factors contribute to excess body fat, which can lead to various health issues.
Managing shortness of breath related to obesity involves maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, staying hydrated, practicing good posture, avoiding airborne irritants, and managing stress. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice is also recommended.