Can Collagen Cause Acne? Skin Health Explored
Medically reviewed by our experts
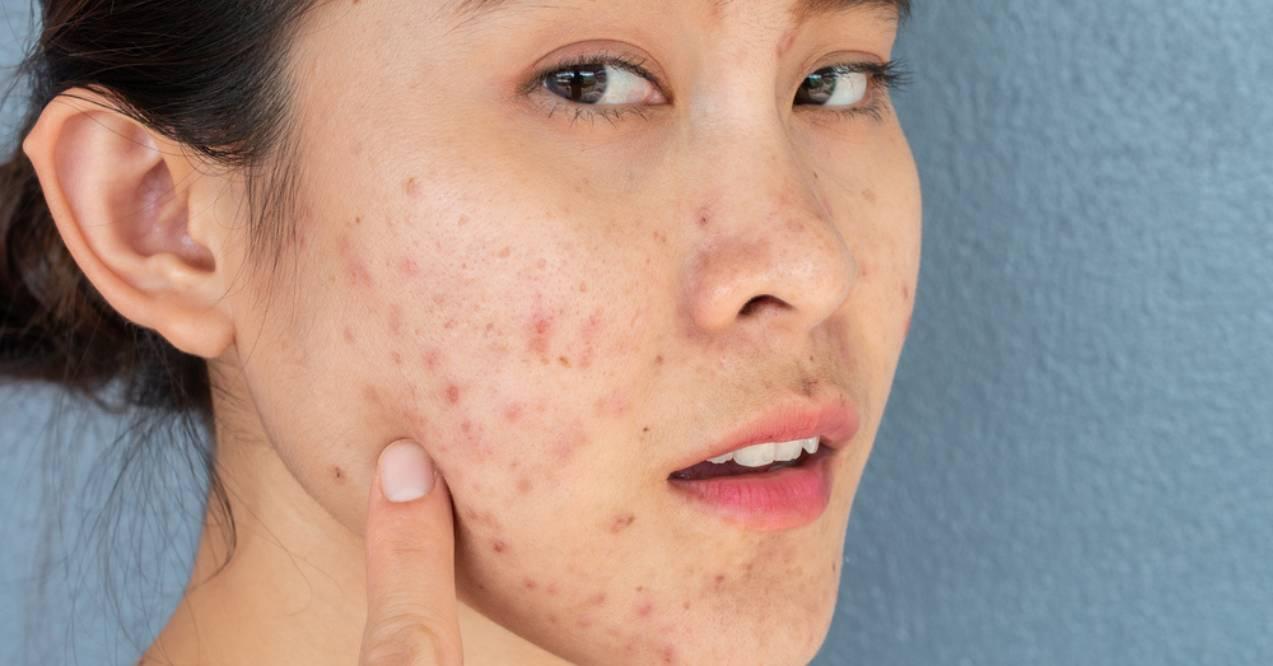

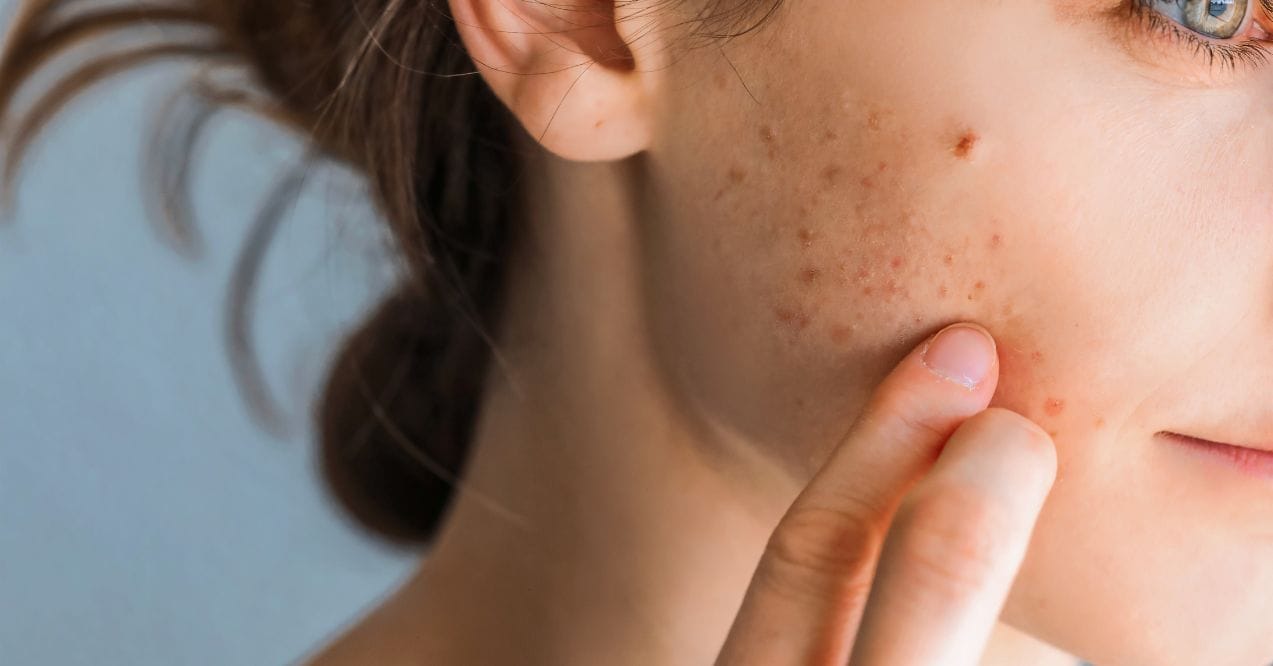
In the pursuit of radiant skin, the question echoes: Can collagen cause acne? Delving into the world of skincare, where every serum and supplement promises a path to a flawless complexion, the relationship between collagen and acne remains a topic of curiosity and debate. Here, we will explore the intricacies of skincare, the link with collagen supplements, and the potential acne issues that emerge in this captivating puzzle.
Collagen, often hailed as a skin savior for its purported benefits in enhancing elasticity and promoting a youthful appearance, stands under the scrutiny of a growing dilemma. Amid the promises of skin rejuvenation, there’s a whisper of uncertainty — does collagen contribute to, or perhaps worsen, acne?
Navigating through the labyrinth of opinions and information, we will seek to unravel the mysteries surrounding this connection. Join us on this journey as we sift through facts and dispel myths, empowering you with the knowledge to make the right decisions about your skincare routine.
What Is Collagen?
Collagen, the unsung hero of our body’s structural integrity, is a fibrous protein that serves as the glue holding us together. This substance plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s form and function and comprises a significant portion of our skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
There are several types of collagen, up to Type V, with Types I, II, and III being the most prevalent. Each type has a distinct function. Type I, found in skin, tendons, and bones, provides structural support. Type II is abundant in cartilage, supporting joint health, while Type III is present in skin, blood vessels, and organs, contributing to elasticity.
In the context of skin health, collagen is like the scaffolding that keeps our skin firm and supple. Collagen production goes down as we age, leading to wrinkles and a loss of that youthful skin glow we know and love. Beyond aesthetics, this substance is crucial for overall well-being. It forms a crucial part of our connective tissues, ensuring joints move smoothly and supporting the strength of bones and muscles.
The skin, being the largest organ, heavily relies on collagen. This protein provides structure, elasticity, and hydration. Imagine collagen as the foundation of a building, holding everything in place. It’s not just about a youthful appearance; it’s about the body’s resilience and ability to heal. Collagen contributes to the skin’s ability to repair and renew itself, making it essential for a healthy and vibrant complexion.
When collagen levels are optimal, the skin retains moisture, stays plump, and resists the formation of fine lines. Beyond aesthetics, collagen supports wound regeneration, contributing to the body’s natural renewal mechanisms. It’s the unseen architect ensuring that, beneath the surface, everything works seamlessly. It’s essential to understand that collagen is not the enemy. In fact, it’s a crucial ally in the pursuit of healthy skin and overall well-being. The challenge lies in unraveling whether certain forms of collagen supplementation might disrupt the delicate balance, leading to concerns like acne.
Collagen Components and Skin Health

Now that we’ve established collagen as a fundamental building block for our body, let’s delve into the fascinating world of collagen peptides and their profound impact on skin health. Collagen peptides are short chains of amino acids derived from the breakdown of larger collagen molecules. These peptides play a crucial role in providing structural support to the skin. As collagen in the form of peptides is ingested or applied topically, it contributes to the synthesis and reformation of collagen fibers, fostering skin elasticity and firmness.
One of the remarkable aspects of collagen peptides is their potential defensive effects against UV-induced photoaging. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can accelerate collagen breakdown, leading to premature aging. Collagen peptides act as a defense mechanism, mitigating the damage caused by UV radiation and supporting the skin’s resilience.
However, it’s crucial to note that the effectiveness of collagen peptides can vary based on individual factors. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and overall skin health play a role in how the body utilizes collagen. While some may experience visible skin texture and firmness improvements, others might not witness the same transformative effects.
Can Collagen Really Cause Acne?
So can collagen cause acne? The relationship between collagen supplementation and acne is a nuanced one. Collagen, in its natural state, is unlikely to be a direct cause of acne. However, certain factors associated with collagen supplements might contribute to acne development in some individuals.
Additives or ingredients in collagen supplements, such as flavorings or preservatives, could potentially trigger skin reactions. Additionally, if collagen supplements lead to an excessive intake of certain nutrients, it might disrupt the delicate balance of the skin, potentially contributing to acne flare-ups.
Alternatively, recent studies have explored a different side of impact of collagen on acne. Some research suggests that collagen supplementation can benefit the skin, promoting hydration, elasticity, and overall complexion.
One factor to consider is the source and type of collagen used in supplements. Collagen supplements are often derived from different sources, including bovine (cow), porcine (pig), marine (fish), and even avian (chicken). Each type comes with its own unique composition, and individual reactions to these sources can differ.
Bovine Collagen
Bovine collagen, for instance, is a popular choice but may carry a risk for those prone to acne. Some individuals report experiencing breakouts after incorporating bovine collagen into their routine. On the contrary, marine collagen, sourced from fish, might be a more favorable option for those concerned about potential acne triggers. Don’t forget that gut health and acne work in symbiosis and a healthy gut usually means clear skin.
Hydrolyzed Collagen
The debate intensifies when considering the processing methods of collagen supplements. Hydrolyzed collagen, broken down into smaller peptides, is believed to be more easily absorbed by the body. However, this form might not be universally suitable, and individuals should remain attentive to how their skin reacts to different types of collagen.
Expert opinions in the field of dermatology vary, reflecting the complexity of this issue. Some dermatologists suggest that when chosen wisely, collagen supplements can enhance skin health without triggering acne. Others emphasize the need for caution, advising individuals to closely monitor their skin’s response to supplementation.
There are many things that can cause acne. Even ashwagandha could cause acne depending on factors like dosage, genetics, and the overall health of those using it. As such, it is important to keep in mind that understanding your body’s needs and responses is key. In the search for acne-free skin, knowledge is your strength.
Tips on Managing Acne While Consuming Collagen Supplements
If you’re keen on reaping the potential benefits of collagen and other skin supplements but are wary of potential acne concerns, fret not. Here are some practical tips to help you navigate this journey while keeping your skin in check:
1. Follow a Healthy Diet

Maintaining a balanced and nutrient-rich diet is fundamental for healthy skin. Go for foods that are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help skin health. At the same time, incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your meals. Hydration is key, too, as it helps flush out toxins and keeps your skin well-hydrated.
2. Adjust the Dose of Collagen

Consider adjusting the dosage of your collagen supplements. It is advisable to start with a smaller dosage when applying skincare products and observe how your skin responds to it. Gradually increasing the dosage allows you to monitor any changes in your skin’s condition. Pay attention to the source and type of collagen as well — experimenting with different varieties might reveal what suits your skin best.
3. Exercise

Regular physical activity not only promotes overall well-being but can also contribute to healthier skin. Sweating during exercise helps cleanse the pores, reducing the likelihood of acne breakouts. Find activities you enjoy, whether it’s jogging, yoga, or dancing, and make them a regular part of your routine. However, there is a common concern among athletes and fitness enthusiasts about supplements: does creatine cause acne? While some people believe that creatine might contribute to acne, scientific evidence on this is inconclusive, and individual reactions can vary.
How Can You Increase Collagen Production for Healthy Skin?
Collagen tends to take a natural dip as we age, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and a loss of elasticity. Fortunately, there are scientifically-backed methods to boost collagen production, promoting healthier skin. Let’s explore some effective strategies and treatments for impactful results:
- Nutrient-Rich Diet – Vitamins and minerals play pivotal roles in collagen production. Berries, nuts, citrus fruits, and leafy greens are excellent dietary sources that contribute to overall skin health.
- Vitamin C Supplementation – Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant known for its role in collagen synthesis. Consider incorporating vitamin C supplements into your routine, especially if your diet may lack sufficient levels of it. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare expert to determine the right dosage for your individual needs.
- Topical Vitamin C Serums – Topically applying vitamin C can also be beneficial. Vitamin C serums are popular in skincare routines for their ability to neutralize free radicals, promote collagen production, and brighten the complexion. Look for products with vitamin C from natural sources, like Camu Camu fruit or Kakadu plum for optimal results.
- Tretinoin (Retin-A) – Tretinoin, a derivative of vitamin A, has been widely studied for its effectiveness in stimulating collagen production and promoting skin renewal. This prescription-based treatment is known for its role in treating acne, but its collagen-boosting properties make it an excellent addition to anti-aging skincare routines. A natural, more skin-friendly, non-clogging alternative is Babchi oil.
- Laser Therapy – Laser treatments have shown promise in stimulating collagen production. These treatments use targeted beams of light to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin and trigger the body’s natural healing response and collagen synthesis. Dermatologists often perform laser therapy in consonance with individual skin types and concerns.
- Microneedling – Microneedling, a minimally invasive procedure, involves the use of fine needles to stimulate collagen production and enhance the absorption of skincare products. Microneedling can be performed by dermatologists or with at-home devices, although professional supervision is recommended for optimal safety and efficacy.
- Peptide-Infused Skincare – Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can mimic the effects of collagen. Incorporating peptide-infused skincare products into your routine can provide an additional boost to collagen synthesis. Search for products containing peptides like palmitoyl pentapeptide-4, which has shown promising results in promoting collagen production.
Conclusion
So can collagen cause acne? Navigating the intricacies of collagen and its potential impact on skin health reveals a complex relationship. While this substance is a crucial ally for healthy skin, the debate on whether collagen supplements can cause acne remains multifaceted. Understanding collagen’s role as the unseen architect of the skin, promoting resilience and renewal, is essential. The type and source of collagen supplements play a pivotal role in determining the individual reactions users may face.
There are insights into collagen’s effectiveness and potential concerns in this matter. Bovine collagen, for example, may pose acne risks, while marine collagen could offer a more favorable option. The processing methods, like hydrolyzation, add another layer of complexity. Expert opinions vary, emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches.
For those venturing into collagen supplementation, mindfulness is key. The journey involves dispelling myths, understanding one’s unique skin response, and consulting professionals. Balancing collagen benefits with acne concerns requires informed decisions, ensuring a holistic approach to skincare that aligns with individual needs.
While collagen itself is not a direct cause of acne, certain factors associated with collagen supplements may contribute to acne development in some individuals.
Collagen, in its natural state, is not typically regarded as a solution for acne.
Collagen supplements are not direct causes of acne. However, additives or an excess of certain nutrients may trigger skin reactions in sensitive individuals if consumed without a proper approach.