Can Alcohol Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes?
Can alcohol cause swollen lymph nodes? Learn about the impact of alcohol on your body and tips for maintaining lymphatic health.


Alcohol is a popular drink, but it can affect your health in many ways. It’s important to know how it impacts your body, especially your immune system and lymph nodes. Your lymph nodes are part of a network that helps fight infections and balance fluids in your body.
In this article, we’ll explore the question: can alcohol cause swollen lymph nodes? We’ll cover the signs to watch for, how doctors diagnose the problem, and ways to keep your lymph nodes healthy. Understanding these effects can help you make better choices about drinking.
Alcohol and the Immune System
Your immune system is your body’s defense team. It protects you from harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses. This system includes white blood cells, antibodies, and organs like the spleen and thymus. They all work together to keep you healthy.
Drinking alcohol can affect how your immune system works. When alcohol enters your blood, it can change how your immune cells behave. If you drink often, it can disrupt important proteins called cytokines. These proteins help your immune cells communicate. Without good communication, your body may struggle to fight off infections.
Alcohol also affects the bacteria in your gut. These bacteria play a big role in keeping your immune system strong. Too much alcohol can upset the balance of these good bacteria. This can lead to inflammation and make it easier for harmful germs to enter your body.

Alcohol and the Lymphatic System
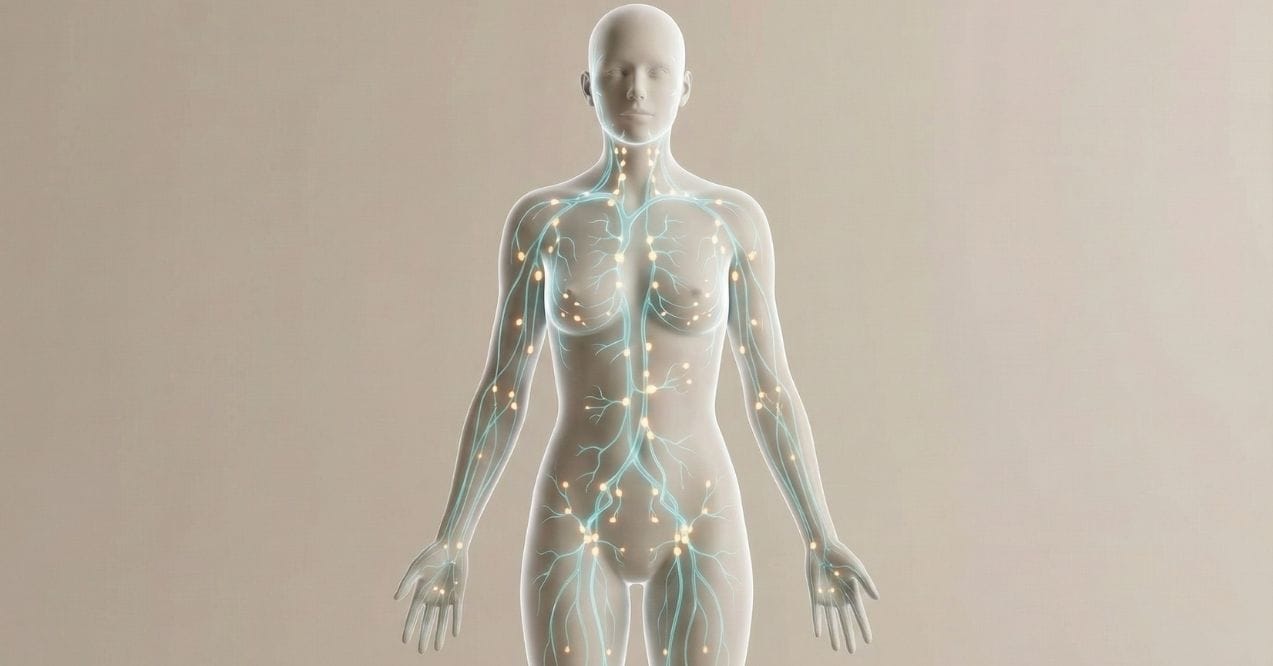
The lymphatic system is crucial for maintaining fluid balance, filtering waste, and supporting the immune system by transporting lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells. Alcohol and lymph nodes are intricately connected, as excessive alcohol consumption can impair the lymphatic system’s function. Alcohol can lead to inflammation and swelling of lymphatic tissues, affecting the flow of lymph and potentially causing lymph nodes to become swollen.
Alcohol also dehydrates the body, which can thicken the lymph fluid, making it more difficult for the lymphatic system to transport waste and toxins efficiently. Over time, this can lead to a buildup of toxins and weakened immune responses. Learning how to clean your lymphatic system, such as through hydration, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can help mitigate some of these negative effects and support overall lymphatic health.
Can Alcohol Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes? Answering the Dilemma

You might wonder, “Can alcohol cause swollen lymph nodes?” While alcohol itself doesn’t directly make your lymph nodes swell, it can set the stage for it to happen. Swollen lymph nodes usually mean your body is fighting an infection or dealing with inflammation.
Alcohol can weaken your immune system, making you more likely to catch infections that could cause swollen lymph nodes. It can also dry you out and irritate your lymphatic tissues, which might lead to swelling. If you drink often, it can harm your liver too. Your liver helps filter out toxins and supports your immune system, so when it’s not working well, it can indirectly affect your lymph nodes.
But remember, swollen lymph nodes usually have other causes, like infections or autoimmune diseases. These are more common culprits than alcohol. If you notice your lymph nodes are swollen and stay that way, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor. They can help figure out what’s really going on and give you the right treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms indicating a problem with the lymphatic system or immune response due to alcohol consumption can include:
- Swollen lymph nodes – Particularly noticeable in areas like the neck, armpits, and groin.
- Frequent infections – Increased susceptibility to colds, flu, and other infections due to a weakened immune system.
- Neck pain after drinking alcohol – Pain or discomfort in the neck area can be associated with swollen lymph nodes or lymphatic inflammation.
- Fatigue – Persistent tiredness or lack of energy, which may be due to the body’s increased effort to fight infections or inflammation.
- Fever – Elevated body temperature as the immune system responds to infections or inflammation.
- Night sweats – Excessive sweating during sleep, often associated with immune response and inflammation.
Prevention of Swollen Lymph Nodes
Preventing the adverse effects of alcohol on the lymphatic and immune systems involves several strategies. By focusing on hydration, diet, alcohol intake, and exercise, you can support these critical systems and maintain better overall health.
1. Stay Hydrated

Can dehydration cause swollen lymph nodes? Dehydration can thicken lymph fluid making it harder for the lymphatic system to transport waste and toxins efficiently. Staying well-hydrated helps mitigate the dehydrating effects of alcohol. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after consuming alcohol, can support lymphatic drainage and reduce the risk of swollen lymph nodes.
2. Maintain a Balanced Diet

A nutritious diet supports the immune system and contributes to overall lymphatic health. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide essential nutrients that bolster immune function.
Additionally, certain foods and herbs for the lymphatic system, such as garlic, ginger, and turmeric, can help reduce inflammation and support lymphatic flow. Maintaining a balanced diet ensures that your body has the necessary resources to combat infections and maintain proper lymphatic function.
3. Decrease Your Alcohol Intake

Reducing alcohol consumption is a direct way to lessen its impact on the immune and lymphatic systems. Moderation is key – consider limiting your alcohol intake to recommended guidelines, such as no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
Taking regular breaks from alcohol, also known as alcohol-free days, can give your body time to recover and reduce the risk of chronic inflammation and immune suppression. If you find it challenging to cut back, seeking support from friends, family, or professional resources can be beneficial.
4. Exercise

Regular physical activity supports lymphatic drainage and boosts the immune system. Exercise stimulates the flow of lymph through the lymphatic vessels, helping to clear toxins and waste from the body. Activities such as walking, jogging, yoga, and stretching can promote lymphatic circulation. Additionally, practices like dry brushing and using essential oils for lymphatic drainage can enhance the effects of exercise. Engaging in consistent, moderate exercise helps maintain a healthy immune response and supports overall lymphatic health.
5. Consider Supportive Supplements
Additionally, incorporating supplements for lymph system health may enhance your lymphatic and immune health. These supplements feature scientifically-backed ingredients that are renowned for their cleansing, detoxifying, and anti-inflammatory properties. Certain ingredients can support immune function, maintain healthy lymph nodes, and promote detoxification, while also helping the proper functioning of lymphatic organs like the spleen and thymus gland.
Discover our premium lymph system supplements collection. Support optimal lymphatic flow, maintain healthy circulation, and promote overall well-being with our scientifically formulated botanical blends.

Conclusion
So, can alcohol cause swollen lymph nodes? While not a direct cause, excessive drinking can weaken your immune system and disrupt your lymphatic system, making you more susceptible to infections and inflammation that lead to swelling.
By prioritizing moderation, staying hydrated, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can support your body’s natural defenses and minimize the negative impacts of alcohol. Remember, knowledge is power – understanding this connection empowers you to make informed choices for a healthier you.
Lymph nodes may swell when you drink wine due to alcohol-induced dehydration and inflammation, weakening the immune system, and increasing susceptibility to infections, all of which can cause lymph nodes to react and become swollen.
Yes, alcohol affects your lymphatic system by causing dehydration and inflammation, which can impair lymph flow. Chronic consumption weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections that can lead to swollen lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes swell due to infections, inflammation, or immune responses. Common triggers include bacterial or viral infections, injuries, and certain medical conditions like autoimmune issues. Swelling is the body’s way of fighting off these threats.
Sign up for our Healthy Living newsletter!
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.