What Is Normal Blood Sugar for Seniors? Understanding Age-Specific Ranges
A common question among older people is “What is normal blood sugar for seniors?” Learn what your optimal blood sugar levels should be and how to naturally keep them in the prime range.


As you age, you might have cause to ask yourself, “What is normal blood sugar for seniors?” Older people can have many health conditions and changing body systems that need attention. One of those is more sensitive blood sugar, which can cause diabetes when out of balance.
What Are Blood Sugar Levels?
Blood sugar levels are often referred to as blood glucose levels. They measure the amount of glucose circulating in your blood at any given time. Glucose is a naturally occurring compound in the human body, and we also get it from food and drink. It’s used for increasing energy levels, so it’s important to have enough. Too much can cause issues, too, so it’s important to monitor glucose levels for seniors as well as anyone who might be at risk for diabetes.
Everyone always has blood sugar running through their bloodstream, whether we’re old or young, diabetic, or not. However, these levels go up and down throughout the day depending on various factors, such as what, how much, and how often we eat, as well as how much physical activity we get, whether we’re stressed, medications we’re taking, how much hydration we receive, and our hormones (just to name a few).
Your body produces a hormone called insulin in the pancreas, an organ in your digestive system. Insulin helps your body maintain proper amounts of blood sugar but as you age, the pancreas sometimes becomes less effective. This means it’s important for people to know the normal blood sugar level for older people.
What Is Normal Blood Sugar Level for Seniors?
It’s important to note that there are varying levels of normal blood sugar for diabetic elderly as well as for those who are healthy and without diabetes.
For healthy people who aren’t diabetic, an optimal blood sugar reading should be about 100 mg/dL first thing in the morning. For a non-diabetic adult who has been fasting for the last eight or so hours (i.e., not consuming anything besides water), that number should be between 80 and 100 mg/dL.
This is usually the lowest level of the day because the person hasn’t eaten anything for a long time. After eating, that number could raise anywhere from 10 to 30 points but should still be in the 90-110 mg/dL range.
During the day, an adult’s blood sugar levels typically range from 90 to 180 mg/dL. If a person takes a reading and it’s below or above this range, they would be categorized as experiencing either low or high blood sugar, each of which has varying effects.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels by Age?
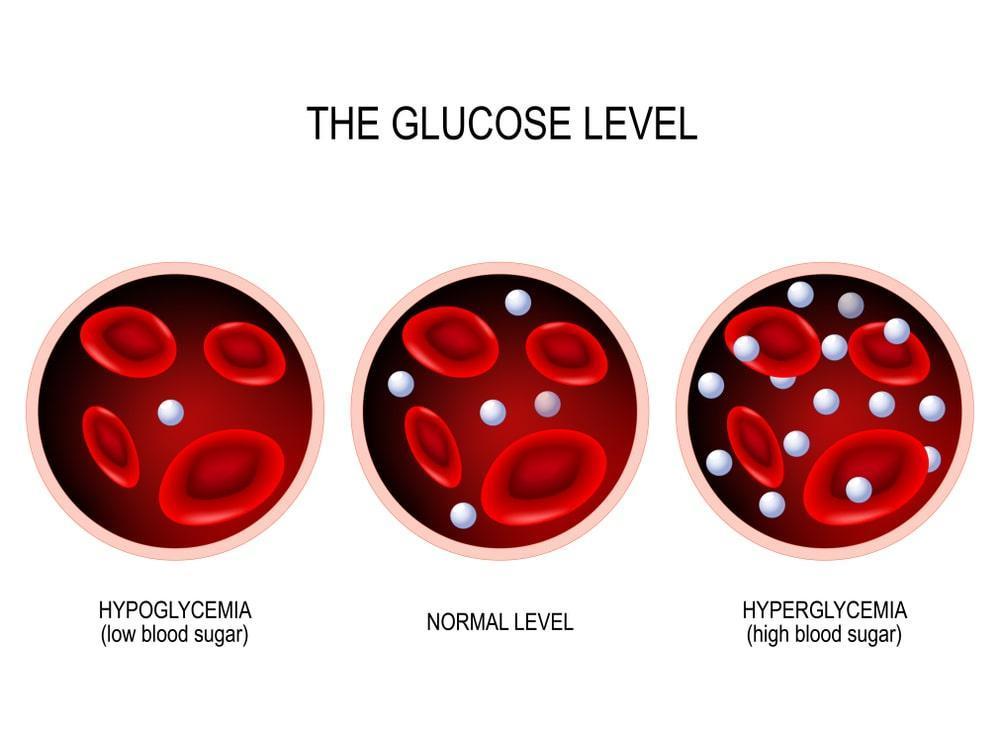
When a person, especially an older person, struggles to maintain adequate blood sugar levels, they can become hypoglycemic. Hypoglycemia, or chronic low blood sugar, can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Endocrine disorders
- Eating disorders
- Type I and Type II diabetes
- Kidney disorders
- Heart conditions
- Liver disease
People experiencing low blood sugar or with a hypoglycemic condition often experience a range of symptoms, such as:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nervousness or shakiness
- Anxiety
- Chills
- Sweating or clammy skin
- Pale tone
- Fainting or tingling in the limbs
Hypoglycemic symptoms should not be ignored, especially in seniors. Medical professionals recommend that seniors not only get checked regularly for signs of diabetes and other conditions but that they are well-versed in the answer to, “What is a normal a1c level for seniors?”
A1c is another term for blood sugar reading. Seniors can check their a1c readings on a glucose meter, which is commonly seen as a finger-prick device that instantly reads a drop of a person’s blood. There are several types of glucose monitoring devices, however, so a person need not ignore their a1c or blood sugar levels for fear of finger pricks.
Hyperglycemia can also be a problem. This is when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels and glucose remains too high in the bloodstream. When this happens, people can experience:
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Headaches
- Blurry vision
- “Unexplained” weight loss
- Difficulty concentrating
These are often signs of diabetes and should be addressed immediately to prevent further health conditions. Additionally, blood sugar fluctuations can contribute to balance issues in elderly individuals, increasing the risk of falls and related injuries. Monitoring blood sugar and A1c levels regularly is key to helping seniors maintain stability, safety, and overall well-being.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for People Over 60
- A healthy older person with average cognitive function and no or few chronic health conditions
- Fasting blood sugar range – 90-110 mg/dL
- Blood sugar range before sleep – 90-150 mg/dL
- An older person with mild to moderate cognitive function and multiple chronic health conditions
- Fasting blood sugar range – 90-150 mg/dL
- Blood sugar range before sleep – 100-180 mg/dL
- An older person with moderate to severe cognitive impairment who has many chronic health conditions (e.g., living in a long-term care facility)
- Fasting blood sugar range – 100-180 mg/dL
- Blood sugar range before sleep – 110-200 mg/dL
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Seniors Over 70
As people get on in age, they might find it even more difficult to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. They often develop various medical conditions, and it might be harder for them to keep up with adequate exercise or a healthy diet.
A person, their caregiver(s), and their medical team should work to form a plan to maintain healthy blood sugar levels at ages 70 and beyond well before they make it to this stage of life. They can come up with easy-to-shop-for recipes that don’t take a lot of time and effort to prepare. They should also have a goal and weekly checklist of exercise and activities that will keep them physically moving and in as prime a state of health as possible. Moreover, understanding what exercises lower blood sugar the fastest can be especially helpful in managing their condition effectively.
A person in their seventies should try to maintain the same blood sugar levels and a1c readings as a person in their sixties.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels for Seniors Over 80
Seniors in their 80s often find it even harder to eat healthfully, stay active, and maintain proper glucose levels than those in their 60s and 70s. As bodies age, systems begin to work more slowly or need more help to function properly.
Thus, it’s even more critical that a person has a plan to prevent themselves from becoming hypoglycemic, hyperglycemic, or diabetic. If they do have diabetes, maintaining optimal elderly a1c glucose levels is more important than ever. They should consume healthy food, try to get the recommended amount of physical activity, take their blood sugar readings often, and possibly add supplements to their nutrition regimen.
If a person finds it difficult to take their readings multiple times a day when in their 80s, they can get a glucose monitoring device worn on the arm or hip that emits continuous readings without needing a finger prick.
Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
In addition to monitoring elderly blood sugar levels, a person can manage their glucose by eating a healthy diet (including plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables as well as whole grains and lean protein) as well as partaking in moderate exercise multiple times a week.

They should of course always take any prescribed medication in the way it is recommended by their doctor. It’s also a good idea for elderly diabetic people to keep glucagon on hand, which can raise blood sugar levels quickly and keep a person from going into insulin shock.
Another way to maintain normal glucose levels for seniors (as well as for other age groups) is by adding natural supplements for blood sugar control such as the one made by PureHealth Research.
This supplement was created by Dr. Holly Lucile, ND and a team of highly experienced and educated researchers who believe that natural compounds can do highly beneficial work to maintain optimal bodily function. This supplement, meant to be taken once a day, has several critical elements that regulate blood sugar, such as:
- Manganese
- Chromium
- Copper
- Zinc
- Biotin
- Magnesium
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
Although this compound hasn’t been shown to have any negative side effects, any person with health conditions should consult their doctor before adding it to their daily regimen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding normal blood sugar ranges for seniors is crucial for managing their overall health. Healthy seniors should aim for fasting blood sugar levels between 90-110 mg/dL and pre-sleep levels of 90-150 mg/dL, while those with chronic conditions may have slightly higher acceptable ranges. Balancing diet, exercise, and medications is essential for maintaining these levels and ensuring optimal health. Tailoring blood sugar goals to individual health needs is key to effective management.
Sign up for our Healthy Living newsletter!
Advertisement. This site offers health, wellness, fitness and nutritional information and is designed for educational purposes only. You should not rely on this information as a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, you should always consult with a physician or other health-care professional. Do not disregard, avoid or delay obtaining medical or health related advice from your health-care professional because of something you may have read on this site. The use of any information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.













